pandas create dataframe
In this tutorial, we’ll explore multiple ways to create a Pandas DataFrame from various Python data structures like lists, dictionaries, NumPy arrays, and more.
It’s based on a tutorial published down below on our YouTube channel.
First let’s import pandas for data manipulation and analysis. We’ll also import supporting libraries like NumPy and JSON for certain examples.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import json
Example 1 - List
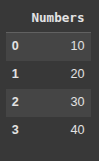
We start with a simple list of numbers
data = [10, 20, 30, 40]
Next we create a pandas DataFrame using the list and we also create a column called “Numbers”
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['Numbers'])
This creates a DataFrame with one column labeled Numbers, containing the values from the list. This method is useful for quickly turning a single list into tabular data.
Example 2
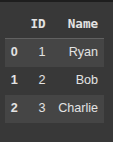
Here, we create a list of lists , where each sublist represents a row of data.
data = [
[1, 'Ryan'],
[2, 'Bob'],
[3, 'Charlie']
]
Next , we create a DataFrame df from data with column names “ID” and “Name”. This turns the list into a table-like structure.
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['ID', 'Name'])
This is great for structured data where each row contains multiple fields.
Example 3 Dictionry Lists
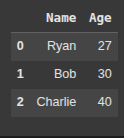
Here, we create a dictionary data with two keys:
- “Name”: list of names.
- “Age””: list of corresponding ages
data = {
'Name': ['Ryan', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [27, 30, 40]
}
Next, we create a DataFrame df from the data dictionary, with columns “Name” and “Age”.
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
This method uses a dictionary, where each key becomes a column name.
Example 4 Passing a series into a dictionary
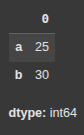
Here we create a pandas Series si with the values [25, 30] and custom index labels ‘a’ and ‘b’
s1 = pd.Series([25, 30], index=['a', 'b'])
Here we create a pandas Series si with the values [‘NY’ , ‘LA’] and custom index labels ‘a’ and ‘b’
s2 = pd.Series(['NY', 'LA'], index=['a', 'b'])
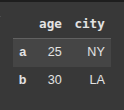
Here we create a dictionary with key value pairs.
the keys being “age” and
“city” and the values are the panda series s1 and s2
data = {
'age': s1,
'city': s2
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
Example 5 tuples
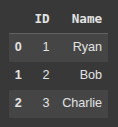
This Creates a lis tof tuples named records, where each tuple holds an ID and a Name.
records = [
(1, 'Ryan'),
(2, 'Bob'),
(3, 'Charlie')
]
Next we create a DataFrame df from the records list of tuples, assigning ‘ID’ and ‘Name’ as column headers.
df = pd.DataFrame.from_records(records, columns=['ID', 'Name'])
Dictionary and List
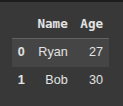
Here, we create a list of dictionaries data, where each dictionary represents a row with keys ‘Name’ and ‘Age’.
data = [
{'Name':'Ryan', 'Age':27},
{'Name':'Bob', 'Age':30}
]
Next, we create a DataFrame df from the list of ditionaries data, with columns ‘Name’ and ‘Age’.
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
Example 7 Two lists
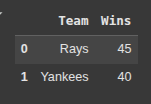
teams = ['Rays', 'Yankees']
wins = [45, 40]
Here, we create a pandas Dataframe with two lists “teams” and “Wins”
df = pd.DataFrame({'Team': teams, 'Wins': wins})
Example 8 from series
Here, we create a Pandas Series with values [10, 20, 30] and default index [0, 1, 2].
s = pd.Series([10, 20, 30])
Here, we create a DataFrame df from Series, with a single column named ‘Values’.
The Series values become the column data.
df = pd.DataFrame(s, columns=['Values'])
Example 9 multiple series
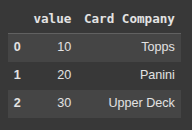
s1 = pd.Series([10, 20, 30])
s2 = pd.Series(['Topps', 'Panini', 'Upper Deck'])
Here, using two panda series, we create a pandas DataFrame df.
df = pd.DataFrame({'value':s1, 'Card Company': s2})
Example 10 CSV
Here, we use panda’s .read_csv() to read a csv file.
df = pd.read_csv("data.csv")
Example 11 excel
Here, we use panda’s .read_excel() to read a csv file.
df = pd.read_excel("data.xlsx")
Example 12 JSON
Here, we use panda’s .read_json() to read a csv file.
df = pd.read_json("data.json")
Example 13 JSON
JSON is used quite a bit when working with APIs or AI, so let’s look at how we can create a Dataframe with it in Pandas.
Here, we import Python’s built-in io module, used for handling in-memory file-like objects e.g text or binary streams.
import io
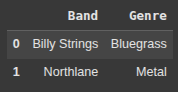
Here, we create a multiline string “json_str” containing a JSON array of band data.
Each item is a dictionary with “Band” and “Genre” Keys.
json_str = '''
[
{"Band":"Billy Strings", "Genre":"Bluegrass"},
{"Band":"Northlane", "Genre":"Metal"}
]
'''
Here, we Parse the “json_str” as JSON using io.StringIO to treat it like a file, and load it into a DataFrame df.
df = pd.read_json(io.StringIO(json_str))
Example 14 custom index
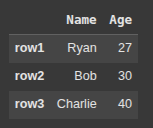
Here, we create a dictionary data with two keys:
“Name” : list of names
“Age”: list of ages.
Used to construct a DataFrame.
data = {
'Name': ['Ryan', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [27, 30, 40]
}
Then we create a DataFrame df from data, setting custom row labels: “row1”, “row2”, and “row3” as the index.
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['row1', 'row2', 'row3'])
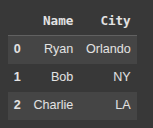
Here, we create a DataFrame “original_df” with columns “Name”, “Age”, and “City”, each containing corresponding values for 3 people.
original_df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Ryan', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [27, 30, 40],
'City': ['Orlando', 'NY', 'LA']
})
Next, we create a new DataFrame “new_df” by selecting only the “Name” and “City” columns from “original_df.
new_df = original_df[['Name', 'City']]
Example 16 row by row
rows = []
Here, we append 3 dictionaries to the rows list, each with keys ‘A’ and ‘B’
for i in range(3):
rows.append({'A': i, 'B': i*10})
Then we create a pandas DataFrame with the rows.
df = pd.DataFrame(rows)
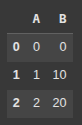
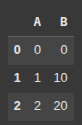
Here, we create an empty DataFrame df with columns ‘A’ and ‘B’, but no rows yet.
df = pd.DataFrame(columns = ['A', 'B'])
Next, we append rows to df in a loop using pd.concat.
Each loop creates a 1-row DataFrame with ‘A’=i and ‘B’=i*10
ignore_index=True resets the index after each concat.
for i in range(3):
df = pd.concat([df, pd.DataFrame({'A': [i], 'B': [i*10]})], ignore_index=True)
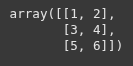
Example 17 numpy array
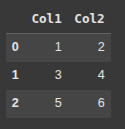
Here, we create a 2D NumPy array, then convert it to a DataFrame df with columns ‘Col1’ and ‘Col2’.
Each inner list becomes a row.
arr = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
df = pd.DataFrame(arr, columns = ['Col1', 'Col2'])
Example 18 sql query
Here, we import Python’s built-in sqlite3 module, used to work with SQLite databases.
import sqlite3
Next, we create a connection “conn” to the SQLite database file names “mydatabase.db”
conn = sqlite3.connect('mydatabase.db')
Here, we run the SQL query “Select * Ffrom users” on the SQLite connection conn,
Then we load the result into a Pandas DataFrame df using the .read_sql_query
query = "Select * From users"
df = pd.read_sql_query(query, conn)
Final Thoughs
These examples demonstrate various ways to create and manipulate DataFrames in Pandas — from basic lists to SQL queries and JSON parsing. Optimizing your workflow with the appropriate method can make your data processing faster and more efficient.
Ryan is a Data Scientist at a fintech company, where he focuses on fraud prevention in underwriting and risk. Before that, he worked as a Data Analyst at a tax software company. He holds a degree in Electrical Engineering from UCF.

[…] then create a dataframe by passing in a dictionary to […]
[…] Before we jump into using concat, we have to import in Pandas and create two dataframes. […]