n8n sort node
Sorting data is a fundamental step in automation workflows. Whether you’re arranging API responses, reordering spreadsheet rows, or creating randomized selections, the Sort node in n8n gives you multiple ways to organize your items.
In this article, we’ll explore how the Sort node works, its different modes, and when to use each.
Before we start, if you are looking for help with a n8n project, we are taking on customers. Head over to our n8n Automation Engineer page.
Why Sorting Matters
Sorting allows you to:
Arrange data in ascending or descending order.
Prioritize items (e.g., latest dates, highest scores).
Randomize outputs for sampling or testing.
Prepare clean, structured results for databases, emails, or dashboards.
How the Sort Node Works
Array sort behavior
n8n’s Sort node uses JavaScript’s built-in Array.sort() method. This means:
Elements are converted to strings by default.
Comparisons are made lexicographically (e.g.,
"100"comes before"2"because"1"is smaller than"2").
If you’re sorting numbers or dates, make sure to configure the Sort node properly or use Code mode for precision.
Configuring the Sort Node
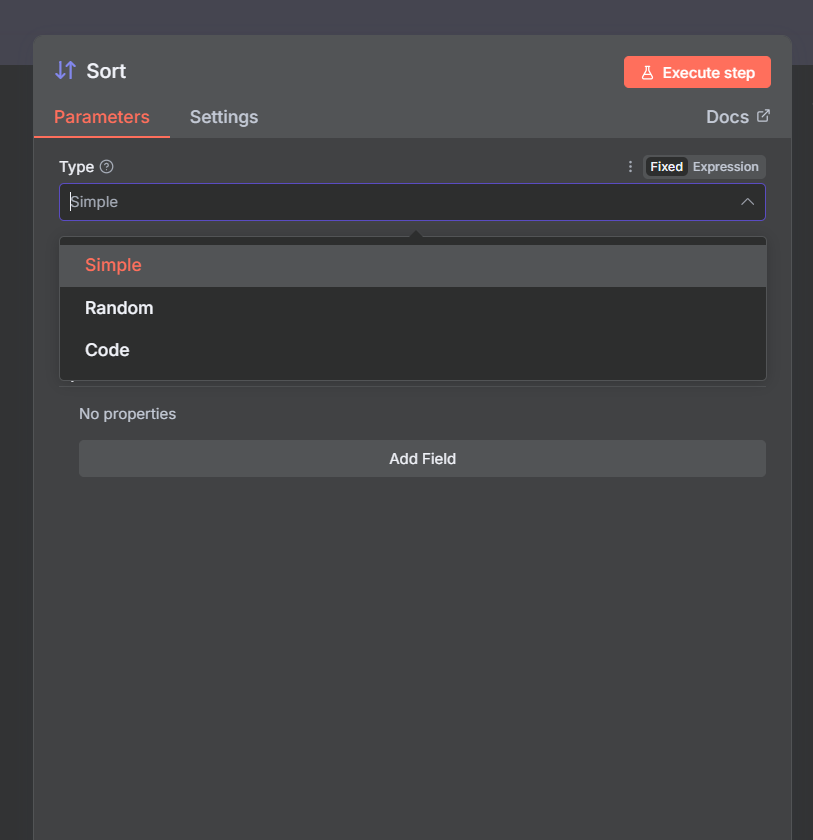
The Type parameter defines how the node sorts items. You can choose between Simple, Random, or Code.
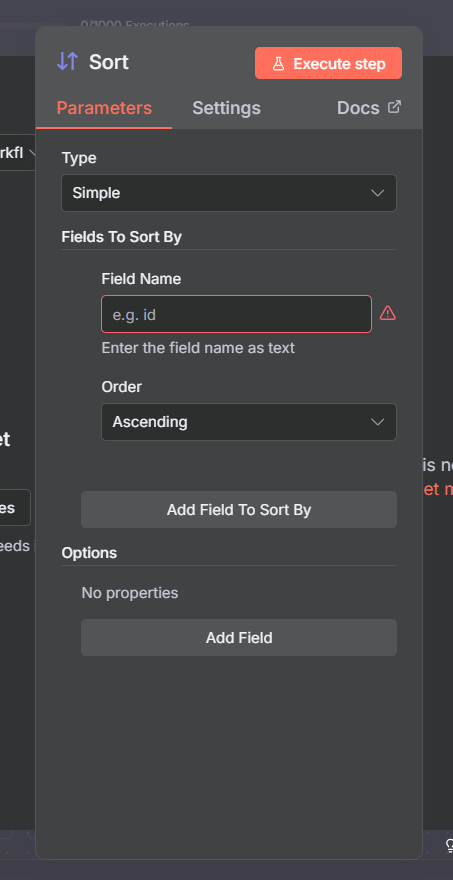
Simple Mode
Performs a straightforward ascending or descending sort based on one or more fields.
How to configure:
Select Type → Simple.
Click Add Field To Sort By.
Enter the Field Name (e.g.,
price,createdAt).Choose Ascending or Descending.
Options in Simple mode:
Disable Dot Notation
Enabled by default, dot notation lets you reference child fields like
user.emailororder.total.Turn it off if your field names contain dots that shouldn’t be treated as nested references.
This is best for sorting one or multiple fields without needing custom logic.
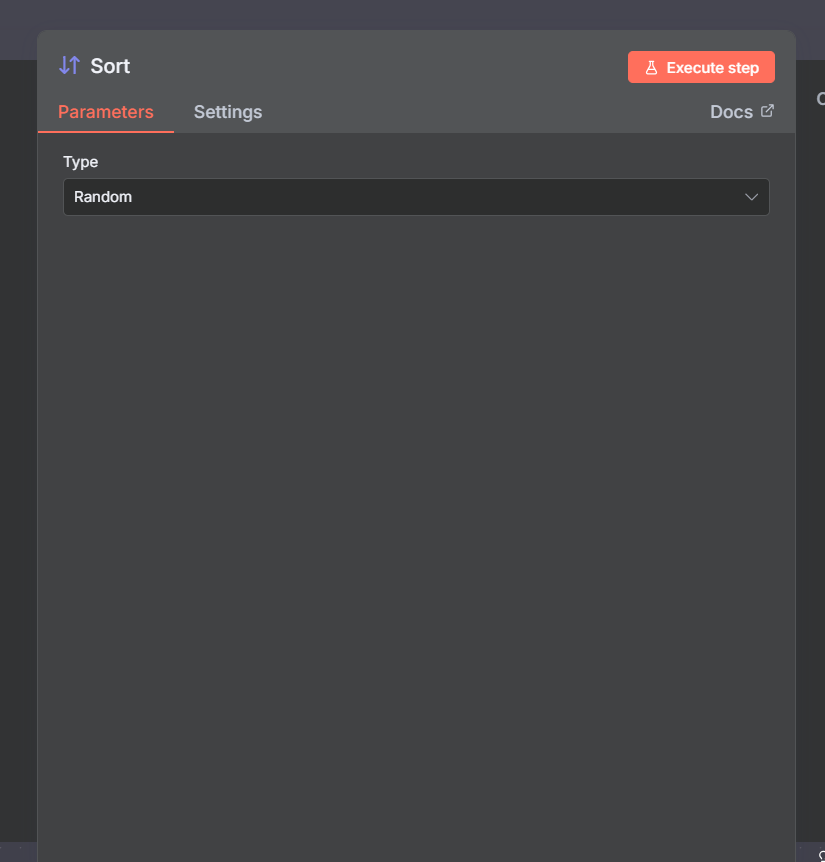
Random Mode
This option creates a random ordering of your list.
How to configure:
Select Type → Random.
Run the workflow — items will shuffle into a new random order.
It’s best for sorting one or multiple fields without needing custom logic.
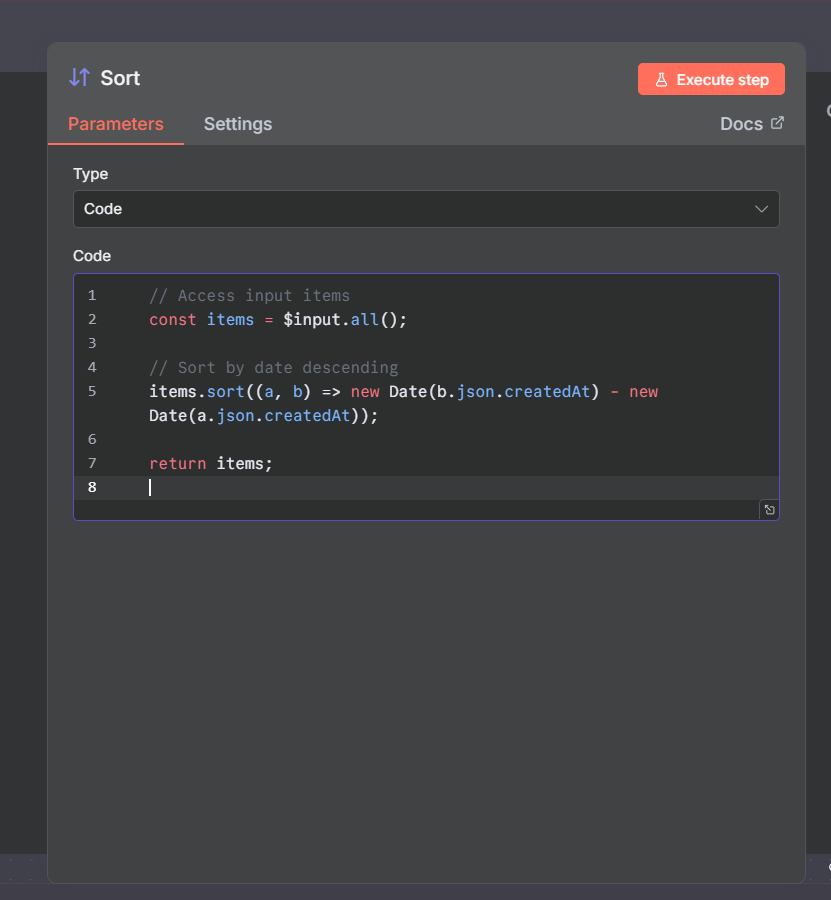
Code Mode
You can add your own JavaScript sorting code for for more flexibility.
How to configure:
Select Type → Code.
Enter your JavaScript code in the Code input field.
example: Here we write code to sort items by createdAt date, newest first.
It is best used for sorting by multiple criteria, Handling nested data and more advanced conditions (e.g sort by different parameters).
Example 1
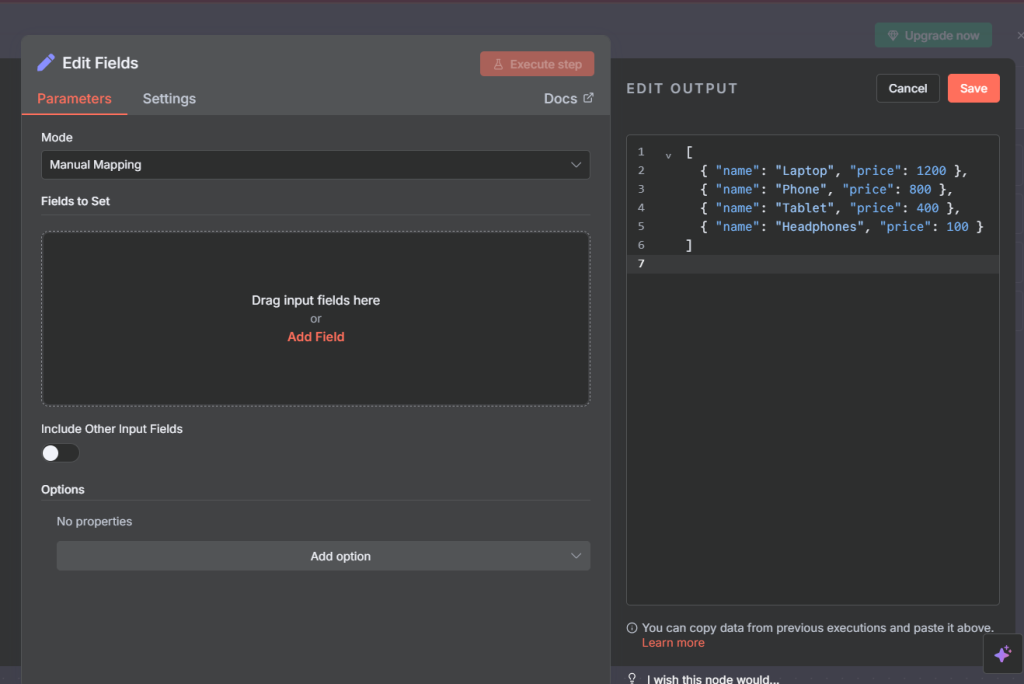
Start with a Field Edit Node (Set Node)
Add a set node and add the following json output as mock up data
[
{ "name": "Laptop", "price": 1200 },
{ "name": "Phone", "price": 800 },
{ "name": "Tablet", "price": 400 },
{ "name": "Headphones", "price": 100 }
]
Next, we add a Sort Node
We add the sort node after the Set Node.
In Type, select Simple,
Click Add Field To Sort By and enter:
Field Name:
priceOrder: Ascending
Ensure the previous node has been executed so you can easily drag and drop the Field Name
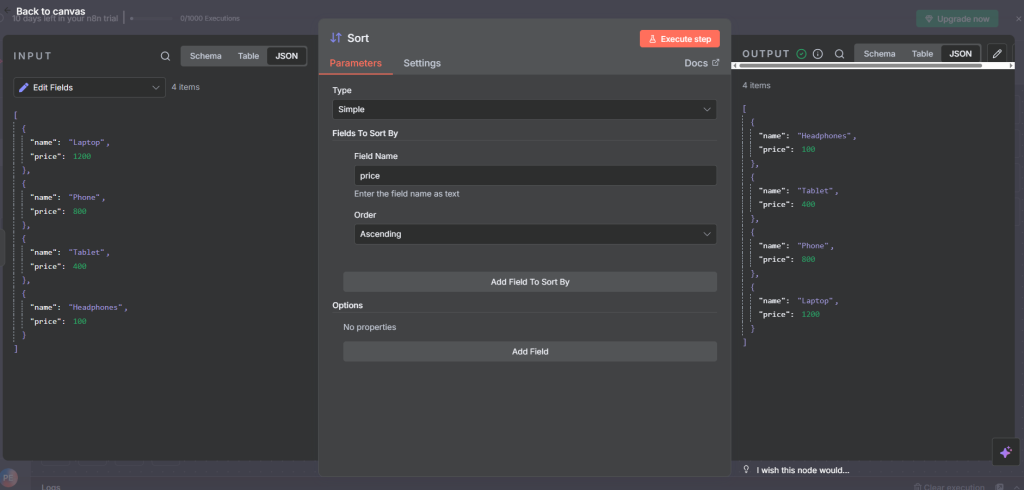
Next, we run the workflow.
After execution, the output will be sorted like this in Ascending order:
[
{ "name": "Headphones", "price": 100 },
{ "name": "Tablet", "price": 400 },
{ "name": "Phone", "price": 800 },
{ "name": "Laptop", "price": 1200 }
]
Example 2
Simple Sort.
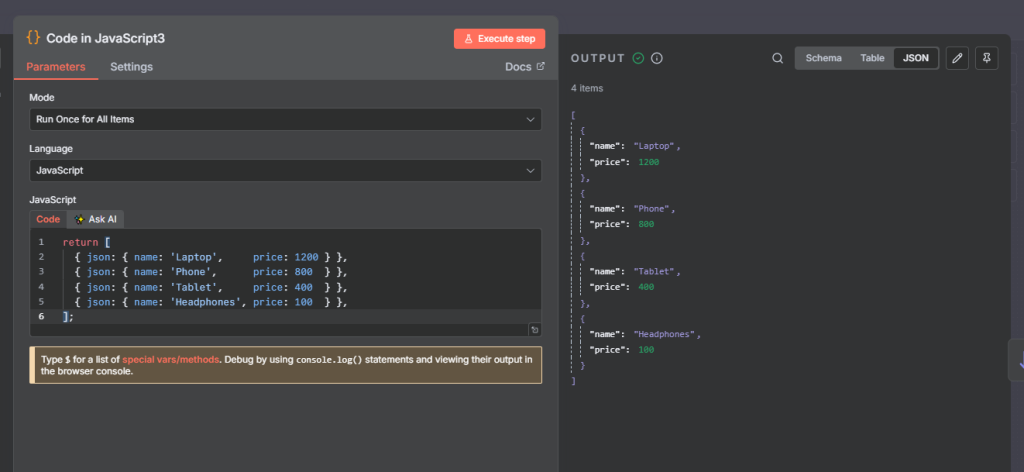
We start with a code node that returns the following json output
return [
{ json: { name: 'Laptop', price: 1200 } },
{ json: { name: 'Phone', price: 800 } },
{ json: { name: 'Tablet', price: 400 } },
{ json: { name: 'Headphones', price: 100 } },
];
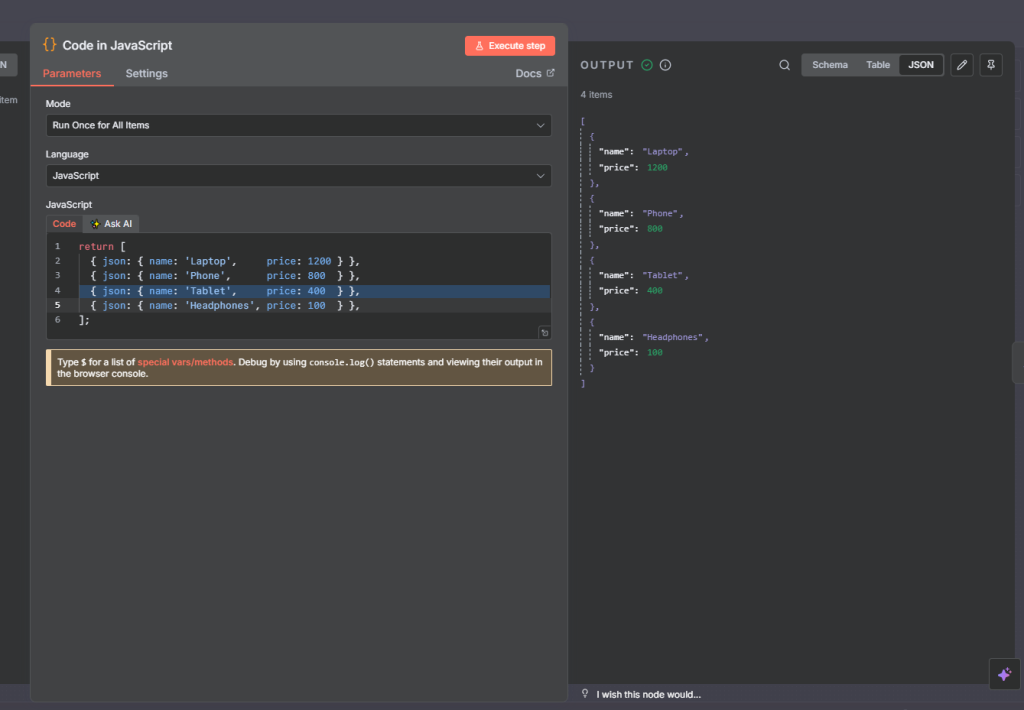
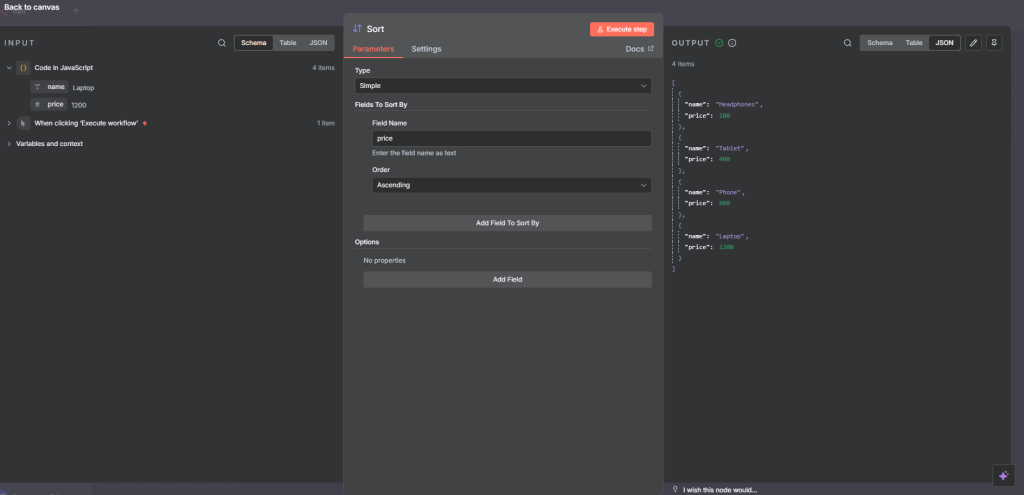
Next we add the sort node and set the Order Ascending ans set the Field Name (i.e the fields to sort by) to price.
The output is a sorted json, sorted by the price in Ascending order.
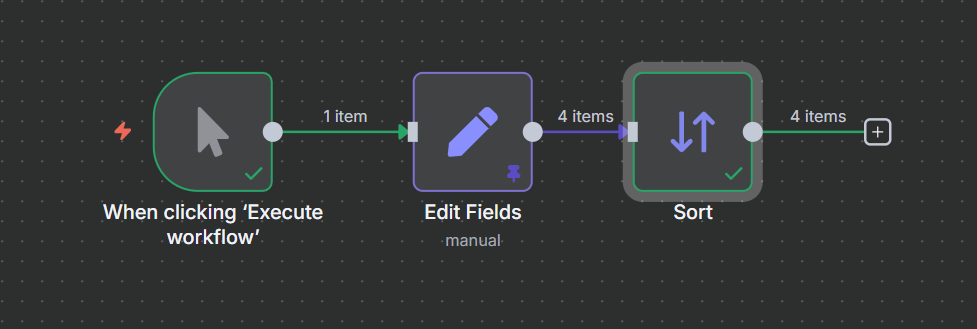
Full flow
Example 3
Let’s sort by the name next which is a string.
First we return similar json outpout as previous example with the code node.
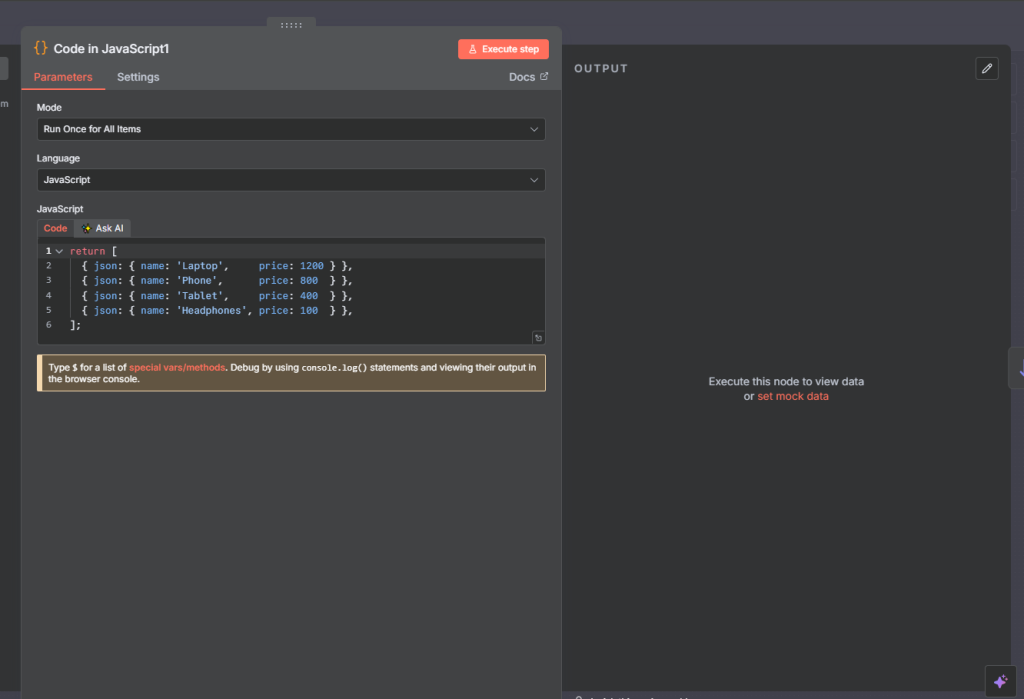
Next, we add a sort node and the
Field Name: price
Order: Ascending
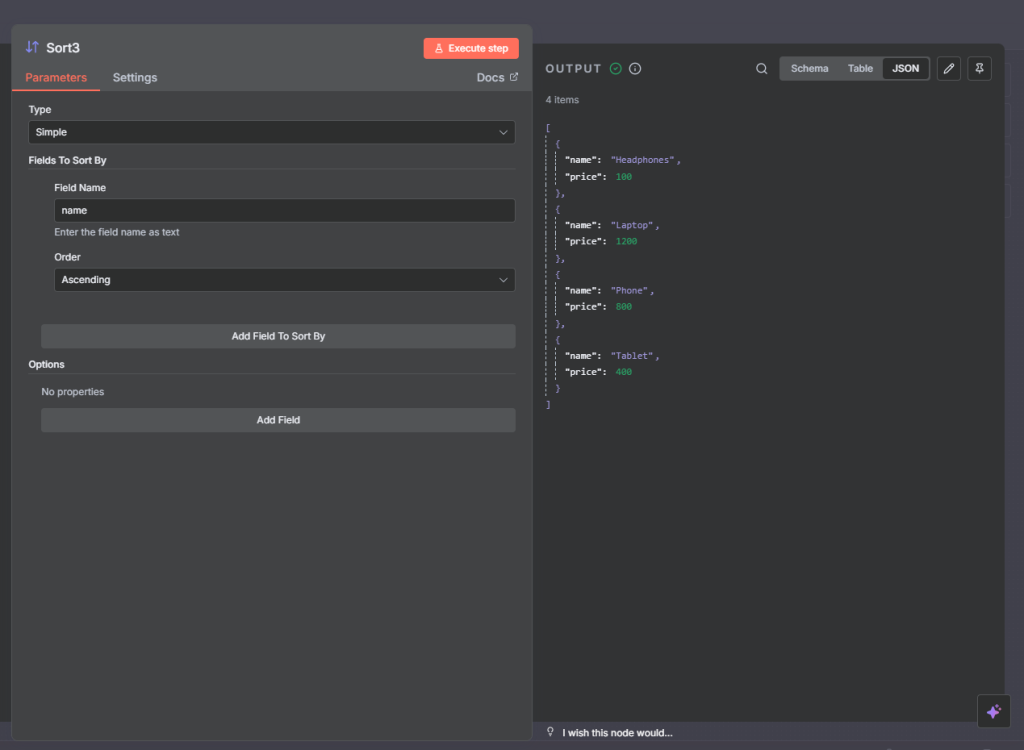
Full flow
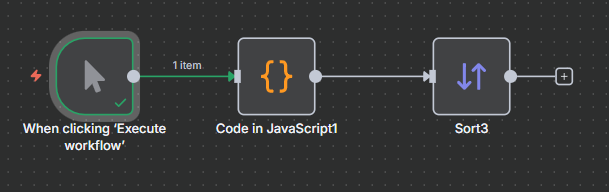
Example 4
Next, lets sort on multiple columns
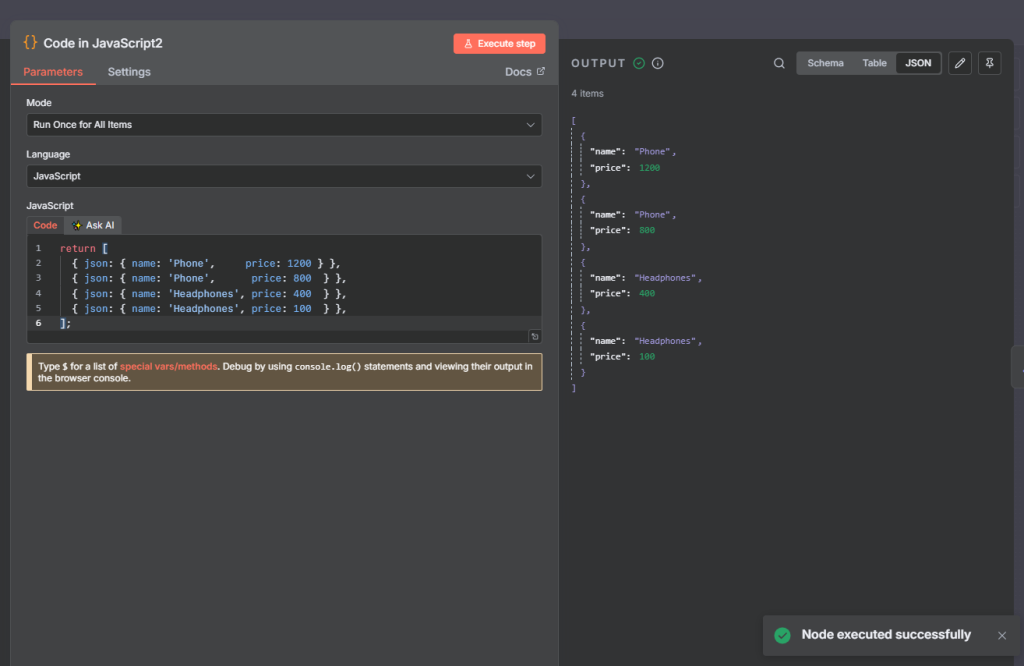
Next we add the sort node with multiple fields to sort by.
in this case we select:
name and price
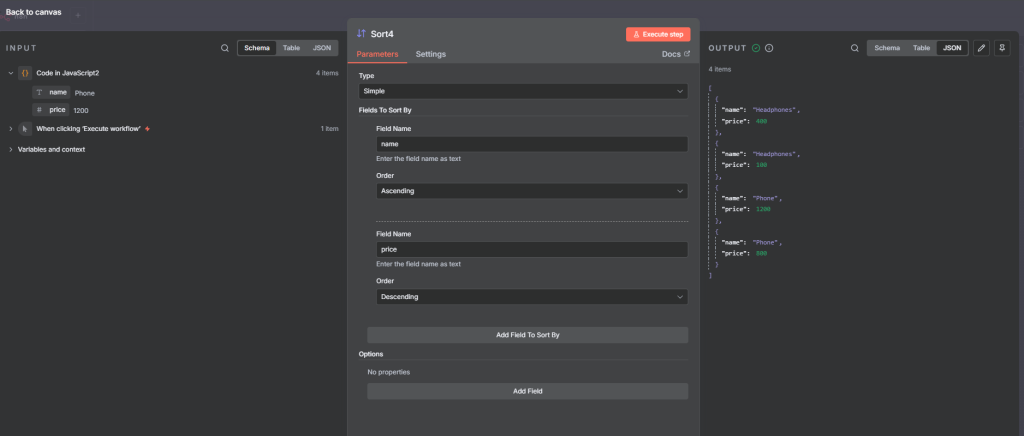
full flow
we should get an output of name and price as follows.
[
{
"name": "Headphones",
"price": 400
},
{
"name": "Headphones",
"price": 100
},
{
"name": "Phone",
"price": 1200
},
{
"name": "Phone",
"price": 800
}
]
Example 5
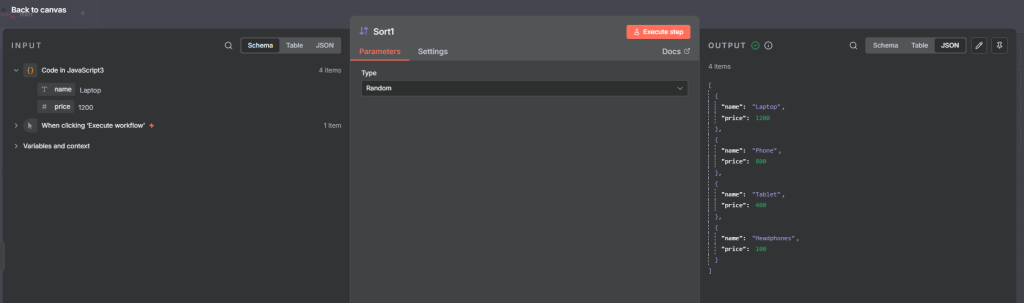
Next, let’s output different data each time.
Next we add the Sort node and select Parameters and select Type as Random.
For the output, we get different data everytime.
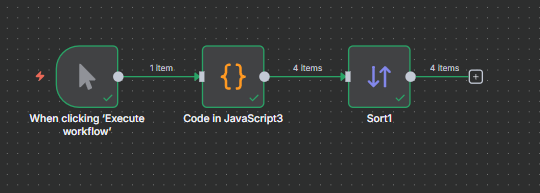
Full flow
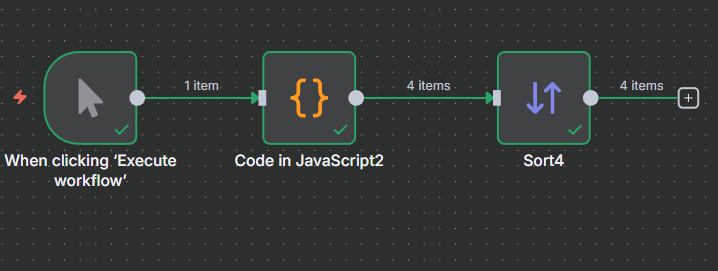
Example 6
We can also add code. But we can only use JavaScript not python.
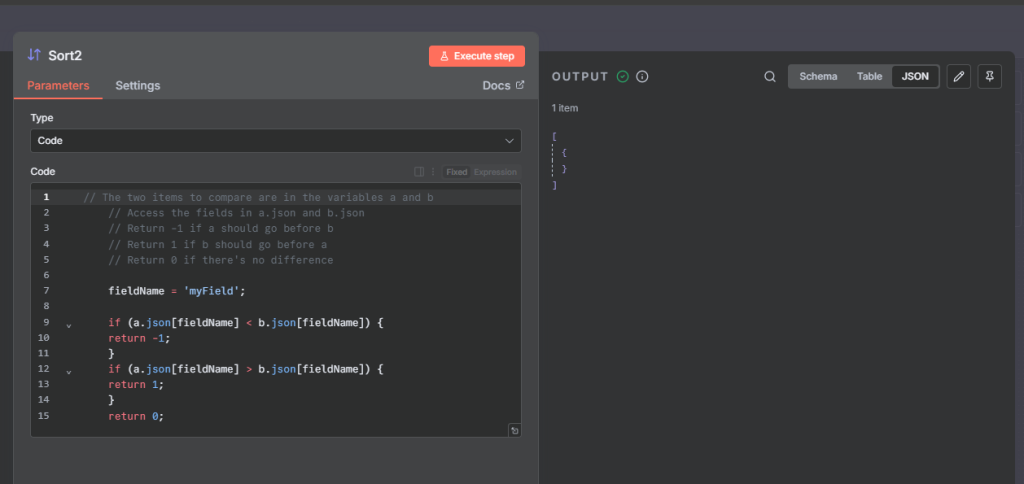
Example 7
More Advanced Example of why we use sort with other nodes.
Example: We can sort the 3 most expensive items.
First, let’s get the code node and return some json data.
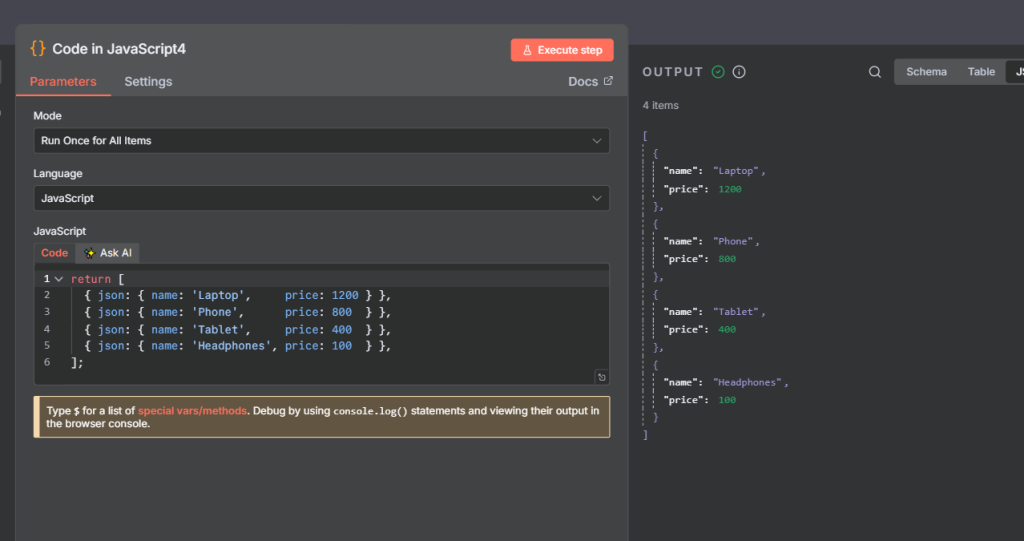
Next, we add the sort node and Field Name to price and order to Ascending.
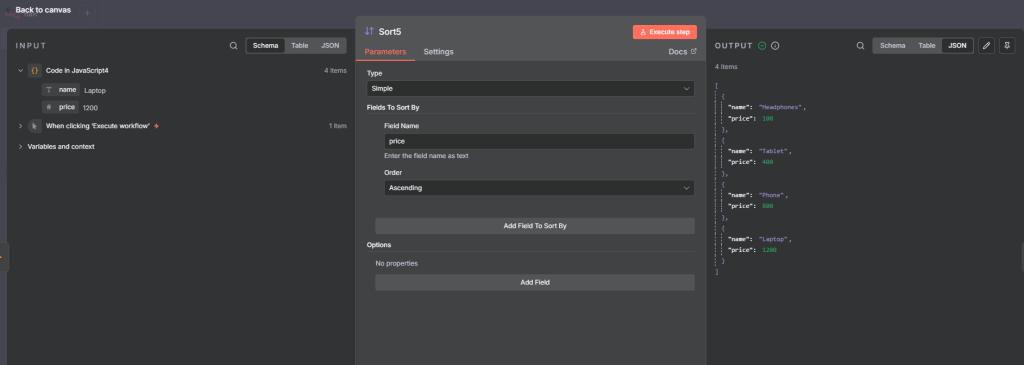
Next we add Limit node and set the Max Items to 3.
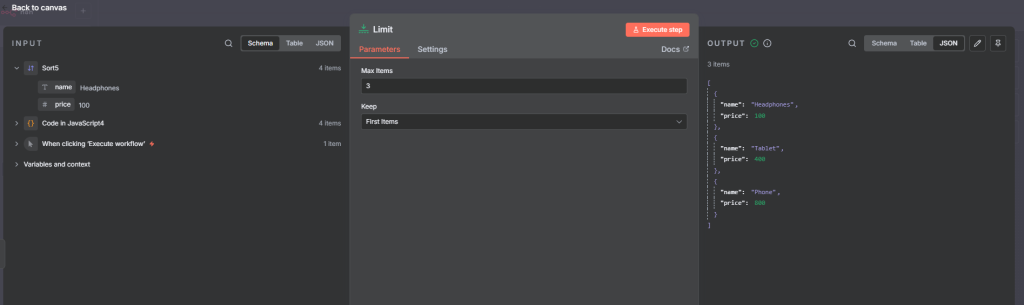
Full flow
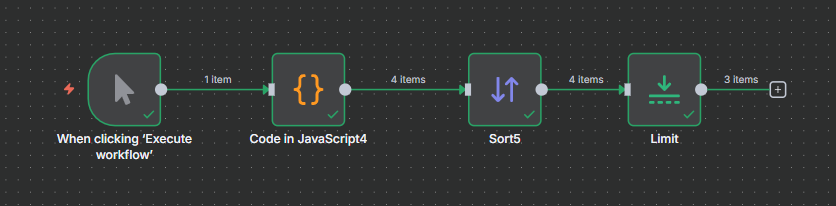
Final thought
The sort node in n8n is a powerful tool for organizing and randomizing your data.
We use Simple for quick sorting (ascending and descending)
We use Random for shuffling items.
We use Code for full control with Javascript
Key notes:
Check your data types: Strings, numbers, and dates may sort differently.
Use Simple mode for quick setups, Random mode for shuffling, and Code mode for custom needs.
When working with large datasets, test on small samples first.
Combine with IF or Merge nodes for more complex logic.
Thank you for reading this article. Make sure to check out our other n8n content on the website. If you need any help with n8n workflows we are taking on customers so reach out
