Augmented Dickey–Fuller test
#import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from statsmodels.tsa.stattools import adfuller
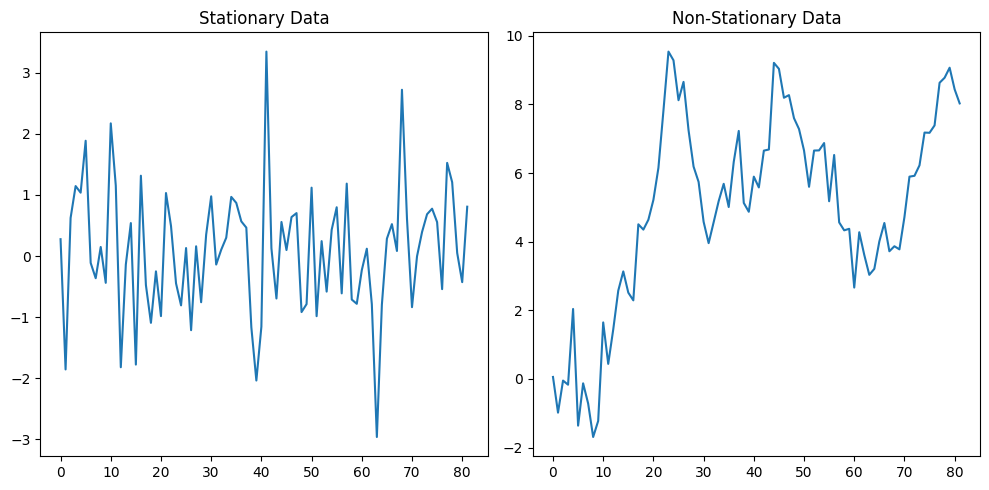
# Generate synthetic stationary and non-stationary data
np.random.seed(17)
# Stationary data: White noise
stationary_data = np.random.normal(size=82)
# Non-stationary data: Random walk
non_stationary_data = np.cumsum(np.random.normal(size=82))
# Plot the data
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(stationary_data)
plt.title('Stationary Data')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(non_stationary_data)
plt.title('Non-Stationary Data')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
parts of the ADF test – tuple
result = adfuller(stationary_data)
print(result)
access by index
print('ADF Test Statistic:', result[0])
print('p-value:', result[1])
print('Number of Lags Used:', result[2])
print('Number of Observations used in the test:', result[3])
print('Critical Values:', result[4])
print('Information Criterion Best:', result[5])
adf_stat, p_value, lags, n_obs, crit_values, ic_best = result
# Function to perform ADF test
def adf_test(series):
result = adfuller(series)
print(f'p-value: {result[1]}')
if result[1] <= 0.05:
print("=> Strong evidence against the null hypothesis, reject the null hypothesis. Data is stationary.")
else:
print("=> Weak evidence against the null hypothesis, fail to reject the null hypothesis. Data is non-stationary.")
adf_test(stationary_data)

adf_test(non_stationary_data)

Ryan is a Data Scientist at a fintech company, where he focuses on fraud prevention in underwriting and risk. Before that, he worked as a Data Analyst at a tax software company. He holds a degree in Electrical Engineering from UCF.
