Streamlit File Uploader
Streamlit File Uploader
st.file_uploader is a Streamlit widget used for uploading files directly from your local system.
It supports single upload or multiple file uploads.
By default st.file_uploader uploaded files are limited to 200MB each.
We can configure this using the server.maxUploadSize config option.
Need a Streamlit developer? Click here
Syntax
st.file_uploader(label, type=None, accept_multiple_files=False, key=None, help=None, on_change=None, args=None, kwargs=None, *, disabled=False, label_visibility=”visible”, width=”stretch”)
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| label | str | Required | The text label displayed above the file uploader. Example: "Upload a CSV". |
| type | str / list | None | Restricts accepted file types. Example: ["csv", "xlsx"]. If None, all file types are allowed. |
| accept_multiple_files | bool | False | If True, allows selecting multiple files at once. Returns a list instead of a single file. |
| key | str / int | None | Unique key to differentiate widgets when using multiple uploaders in the same app. |
| help | str | None | Tooltip message shown when the user hovers over an info icon next to the uploader. |
| on_change | callable | None | A callback function that triggers when a file is uploaded. |
| args | tuple | None | Arguments to pass to the on_change callback. |
| kwargs | dict | None | Keyword arguments to pass to the on_change callback. |
| disabled | bool | False | If True, disables the uploader so users cannot interact with it. |
| label_visibility | str | "visible" | Controls label visibility. Options: "visible", "hidden", "collapsed". |
| width | str | "stretch" | Defines uploader width. Options: "small", "medium", "large", "stretch". |
Basic Upload App
import streamlit as st
st.title("Streamlit File uploader")
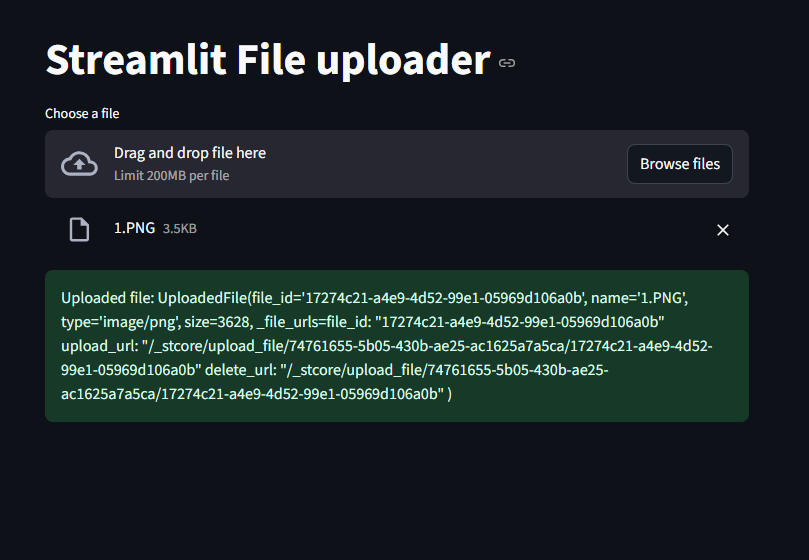
uploaded_file = st.file_uploader("Choose a file")
#we check if there's an uploaded file. if there is, we display a success message
if uploaded_file is not None:
st.success(f"Uploaded file: {uploaded_file}")
Uploading a Single File
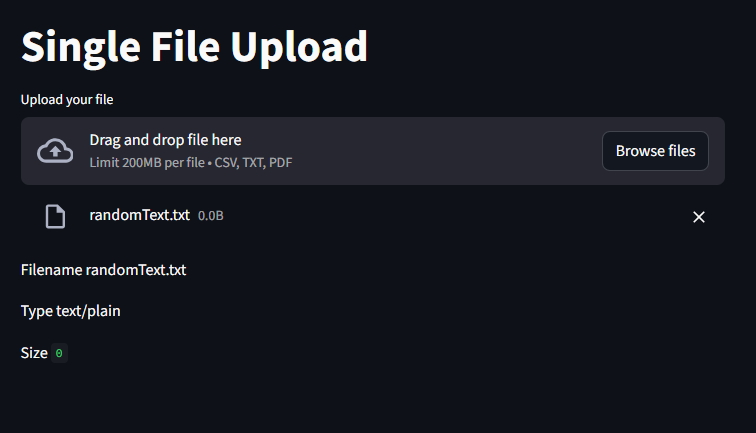
I created an empty .txt file called randomText
import streamlit as st
st.title("Single File Upload")
uploaded_file = st.file_uploader("Upload your file", type=["csv", "txt", "pdf"])
if uploaded_file is not None:
st.write("Filename", uploaded_file.name)
st.write("Type", uploaded_file.type)
st.write("Size", uploaded_file.size)
Allowing Multiple Files
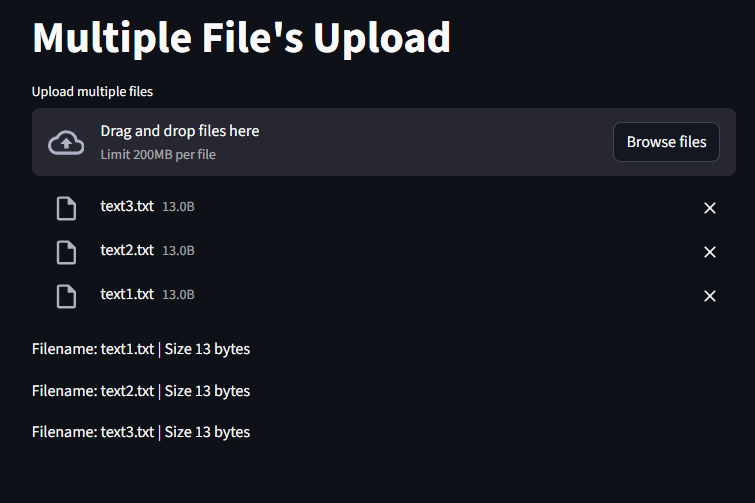
We need to set ” accept_multiple_files” to True if we want to upload multiple files at once.
st.title("Multiple File's Upload")
uploaded_files = st.file_uploader("Upload multiple files", accept_multiple_files=True)
if uploaded_files:
for file in uploaded_files:
st.write(f"Filename: {file.name} | Size {file.size} bytes")
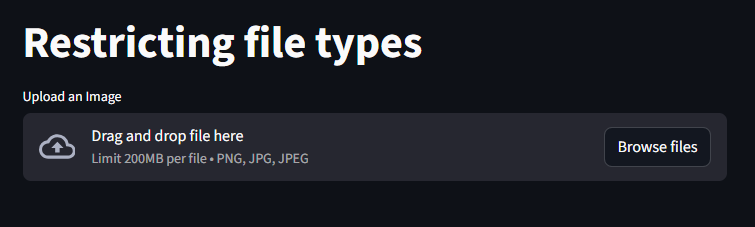
Restricting file Types
we use the “type” parameter to control allowed file formats:
if we click on the “Browse files button, we would see that it only permits images. it would not show files that are not images”
st.title("Restricting file types")
st.file_uploader("Upload an Image", type=["png", "jpg", "jpeg"])
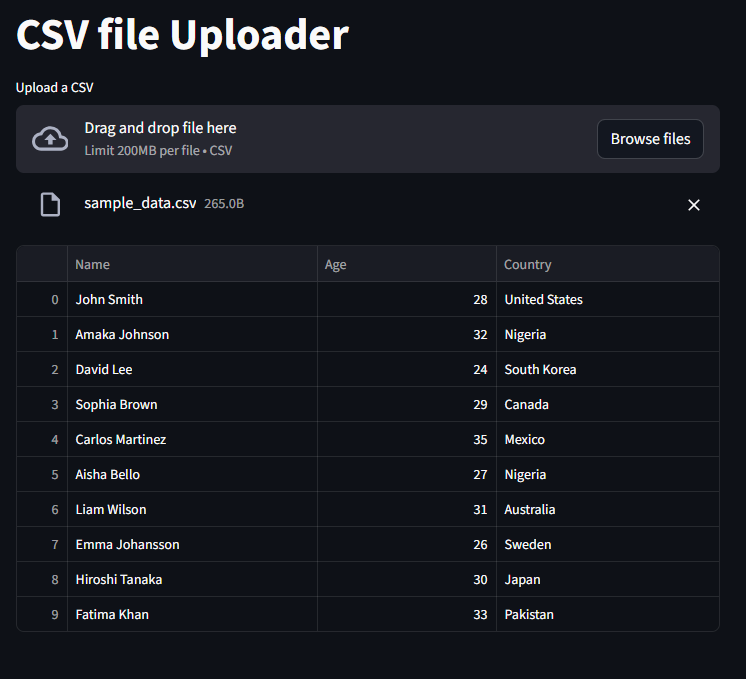
Uploading and Displaying CSV Files
we can upload and view csv files by combining st.file_uploader with pandas
And of course we have to set the type to csv
import pandas as pd
import streamlit as st
st.title("CSV file Uploader")
csv_file_upload = st.file_uploader("Upload a CSV", type=["csv"])
if csv_file_upload is not None:
df = pd.read_csv(csv_file_upload)
st.dataframe(df)
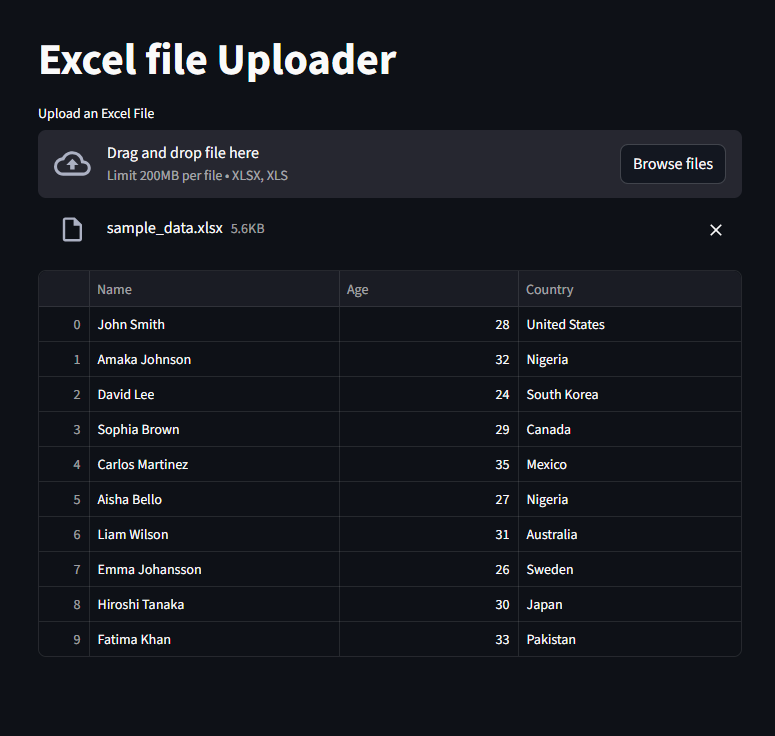
Uploading and Displaying Excel Files
we can upload and view excel files by combining st.file_uploader with pandas
And of course we have to set the type to xlsx and xls
import pandas as pd
import streamlit as st
st.title("Excel file Uploader")
excel_file_upload = st.file_uploader("Upload an Excel File", type=["xlsx", "xls"])
if excel_file_upload is not None:
df = pd.read_excel(excel_file_upload)
st.dataframe(df)
Uploading and Displaying Images
import streamlit as st
#we import Image from PIL
from PIL import Image
st.title("Image Uploader")
image_file = st.file_uploader("Upload an Image", type=["png", "jpg", "jpeg"])
if image_file is not None:
image = Image.open(image_file)
st.image(image, caption="Uploaded Image", use_container_width=True)

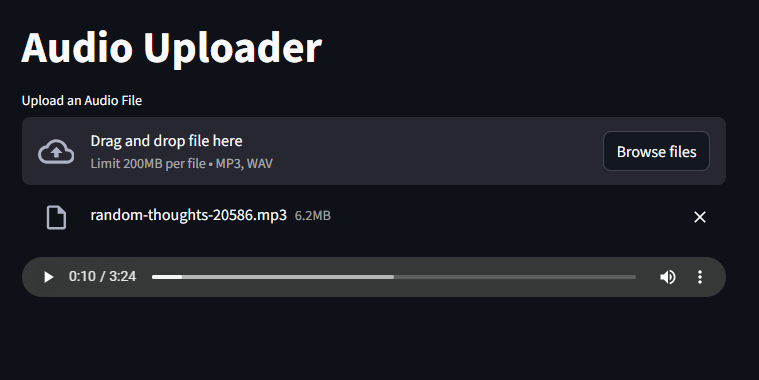
Uploading and Playing Audio Files
import streamlit as st
st.title("Audio Uploader")
audio_file = st.file_uploader("Upload an Audio File", type=["mp3", "wav"])
if audio_file is not None:
st.audio(audio_file, format="audio/mp3")
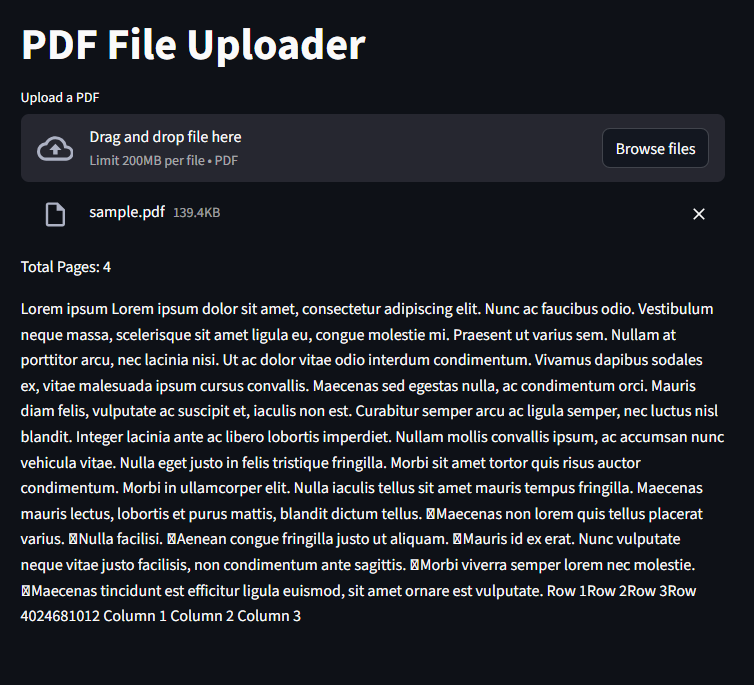
Uploading and Viewing PDFs
import streamlit as st
from PyPDF2 import PdfReader
st.title("PDF File Uploader")
pdf_file = st.file_uploader("Upload a PDF", type=["pdf"])
if pdf_file is not None:
pdf_reader = PdfReader(pdf_file)
st.write(f"Total Pages: {len(pdf_reader.pages)}")
# Display the first page
first_page = pdf_reader.pages[0]
st.write(first_page.extract_text())
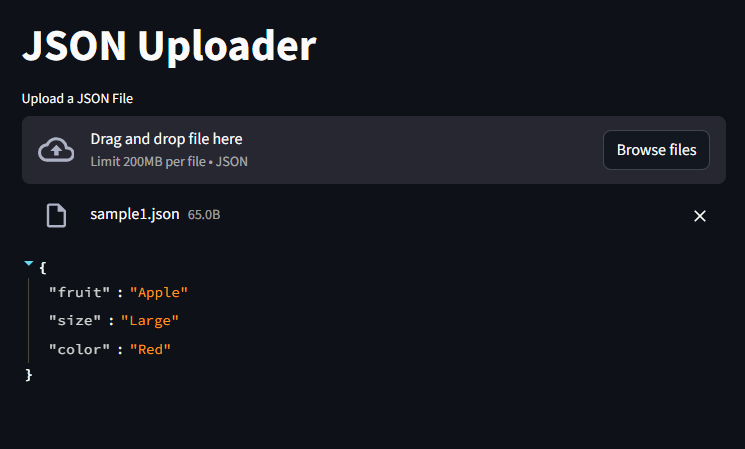
Uploading JSON Files
import streamlit as st
import json
st.title("JSON Uploader")
json_file = st.file_uploader("Upload a JSON File", type=["json"])
if json_file is not None:
data = json.load(json_file)
st.json(data)
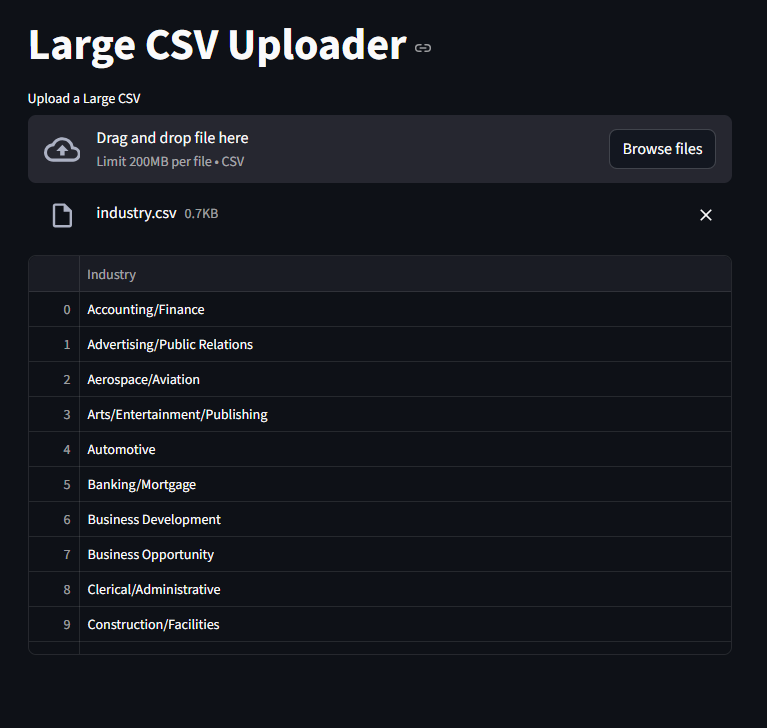
Reading Large CSV files Efficiently
we can set the chunk size to limit how we view the files
The chunksize parameter tells Pandas to read the CSV file in smaller portions (chunks) instead of loading the entire file into memory at once.
:
import pandas as pd
import streamlit as st
st.title("Large CSV Uploader")
csv_file = st.file_uploader("Upload a Large CSV", type=["csv"])
if csv_file is not None:
chunks = pd.read_csv(csv_file, chunksize=5000)
df = pd.concat(chunks)
st.dataframe(df)
Handling Multiple File Types Together
we can handle multiple file types upload by using basic python logic
import streamlit as st
import pandas as pd
from PyPDF2 import PdfReader
from PIL import Image
st.title("Multi-File Type Handler")
file = st.file_uploader("Upload CSV, Image, or PDF", type=["csv", "png", "pdf"])
if file:
if file.type == "text/csv":
df = pd.read_csv(file)
st.dataframe(df)
elif file.type == "application/pdf":
pdf_reader = PdfReader(file)
st.write(pdf_reader.pages[0].extract_text())
elif "image" in file.type:
image = Image.open(file)
st.image(image)

