Streamlit dropdown
Dropdowns are compact ways to present multiple options, prevents invalid inputs and it’s great for filtering and navigation.
we can have two types of dropdowns in streamlit
st.selectbox: single selection
st.multiselect: multiple selections
Need a Streamlit developer?: Click here
Simple Selectbox
import streamlit as st
option = st.selectbox(
"Choose an item",
["Bag", "Shoe", "Watch", "Cup"]
)
st.write("you selected", option)
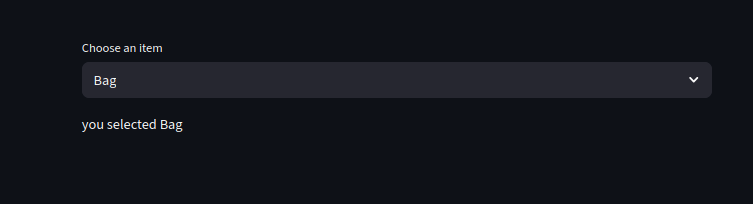
Basic dropdown features
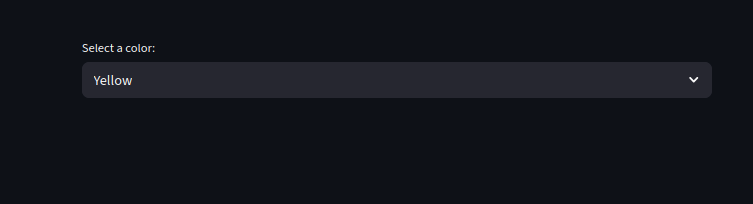
we can set a default value, customize labels and values and enable search within dropdowns
import streamlit as st
colors = ["Red", "Green", "Blue", "Yellow"]
color = st.selectbox(
"Select a color:",
options=colors,
index=3 #i.e the default color is yellow
)
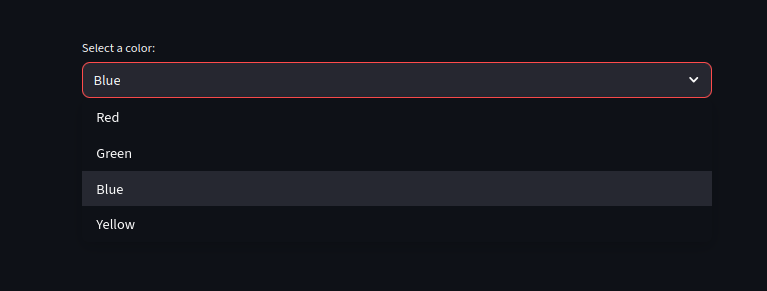
Using Multiselect
We can use multiselect to select multiple options.
We can also use it to filter
import streamlit as st
languages = st.multiselect(
"Select languages you know:",
["Python", "Java", "C++", "Rust", "Go"]
)
st.write("You selected:", languages)
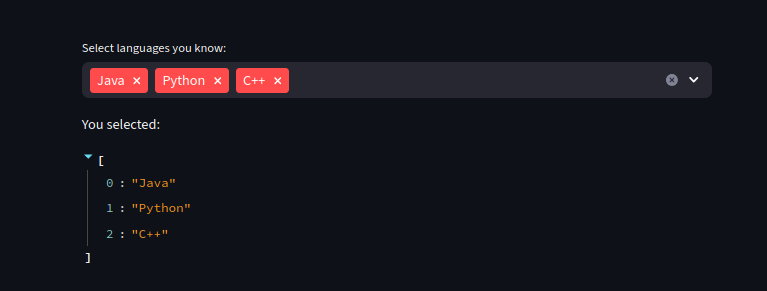
Dropdowns with Dynamic Data
we can generate options from a list, dict or Dataframe
Let’s generate data from a pandas column
import pandas as pd
import streamlit as st
df = pd.DataFrame({
"City": ["London", "Paris", "New York", "Tokyo"],
"Country": ["UK", "France", "USA", "Japan"]
})
city = st.selectbox("Select a city", df["City"])
st.write("You selected:", city)
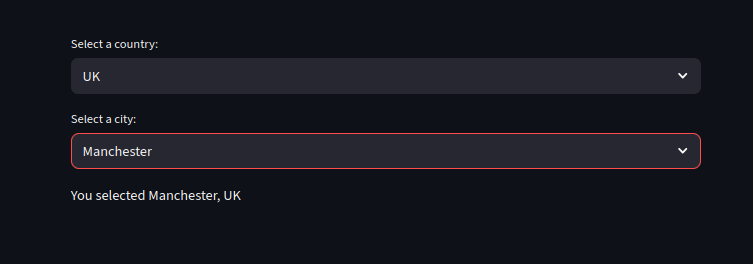
Dependent Dropdowns (Chained Filters)
import streamlit as st
countries = {
"USA": ["New York", "Los Angeles", "Chicago"],
"India": ["Delhi", "Mumbai", "Bangalore"],
"UK": ["London", "Manchester", "Liverpool"]
}
#we use countries .keys() to get the Countries since its a python dictionary
#list just shows it in a list dropdown
country = st.selectbox("Select a country:", list(countries.keys()))
#This list the cites of the selected country
city = st.selectbox("Select a city:", countries[country])
st.write(f"You selected {city}, {country}")
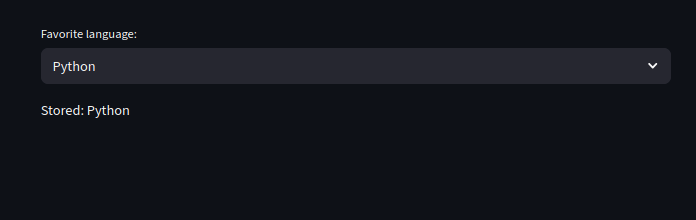
import streamlit as st
if "fav_lang" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.fav_lang = "Python"
st.session_state.fav_lang = st.selectbox(
"Favorite language:",
["Python", "JavaScript", "Rust"],
index=["Python", "JavaScript", "Rust"].index(st.session_state.fav_lang)
)
st.write("Stored:", st.session_state.fav_lang)
Dropdowns + Session State
we can preserve selected values across reruns
import streamlit as st
if "fav_lang" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.fav_lang = "Python"
st.session_state.fav_lang = st.selectbox(
"Favorite language:",
["Python", "JavaScript", "Rust"],
index=["Python", "JavaScript", "Rust"].index(st.session_state.fav_lang)
)
st.write("Stored:", st.session_state.fav_lang)
Dropdowns in Forms
import streamlit as st
with st.form("fruits and prog lang survey form"):
fruit = st.selectbox("Favorite fruit:", ["Apple", "Mango", "Banana"])
lang = st.multiselect("Languages:", ["Python", "C++", "Go"])
submit = st.form_submit_button("Submit")
if submit:
st.write("Results:", fruit, lang)
Conclusion
For large datasets (e.g., thousands of options):
Use caching (st.cache_data) for dropdown options
Consider search boxes (st.text_input) instead
Paginate or group dropdown values
Want to learn more on Streamlit?: Click here
Watch Videos on Streamlit:
