Streamlit Number Input
The st.number_input() widget in Streamlit allows users to input numeric values such as integers or floats.
When should it be implemented?
Acquiring numerical input from users.
Obtaining budgets, quantities, or percentages.
Price ranges are acceptable.
Developing interfaces that are dynamic.
Need a Streamlit Developer? Click Here
Syntax
st.number_input(label, min_value=None, max_value=None, value=”min”, step=None, format=None, key=None, help=None, on_change=None, args=None, kwargs=None, *, placeholder=None, disabled=False, label_visibility=”visible”, icon=None, width=”stretch”)
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| label | str | Required | The label displayed above the number input box. |
| min_value | int / float | None | The minimum allowed value. If None, there’s no lower limit. |
| max_value | int / float | None | The maximum allowed value. If None, there’s no upper limit. |
| value | int / float | min | The initial value. By default, it equals min_value if provided, otherwise 0. |
| step | int / float | 1 | The increment/decrement step when using arrows or typing. |
| format | str | None | Defines how the number is displayed. Example: "%0.2f" for two decimal places. |
| key | str | None | A unique key to maintain the widget’s state. |
| help | str | None | Tooltip text that appears when hovering over the input. |
| on_change | callable | None | A callback function triggered when the input value changes. |
| args | tuple | None | Additional positional arguments passed to the on_change callback. |
| kwargs | dict | None | Additional keyword arguments passed to the on_change callback. |
| placeholder | str | None | Text displayed when the input field is empty. |
| disabled | bool | False | If True, disables the input field and makes it uneditable. |
| label_visibility | str | "visible" | Controls label display. Options: "visible", "hidden", or "collapsed". |
| icon | str | None | Displays an icon inside the input box. (Available in recent Streamlit versions) |
| width | str | "stretch" | Controls the width of the input box. You can also pass fixed widths like "300px". |
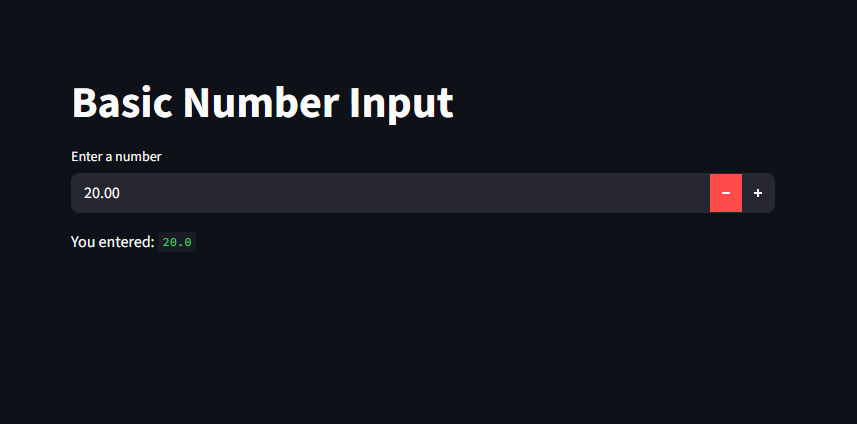
Basic Example
import streamlit as st
st.title("Basic Number Input")
number = st.number_input("Enter a number")
st.write("You entered:", number)
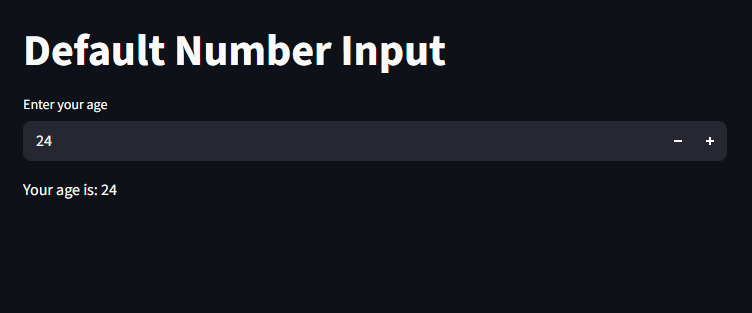
Setting Default values
you can set a default value for the input
import streamlit as st
st.title("Default Number Input")
age = st.number_input("Enter your age", value=24)
st.write(f"Your age is: {age}")
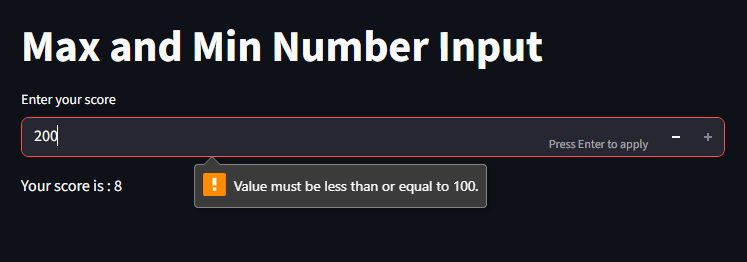
Setting Minimum and Maximum Values
you can restrict the range of numbers users can enter
setting the max and min value prevents invalid inputs automatically
import streamlit as st
st.title("Max and Min Number Input")
score = st.number_input("Enter your score", min_value=0, max_value=100)
st.write(f"Your score is : {score}")
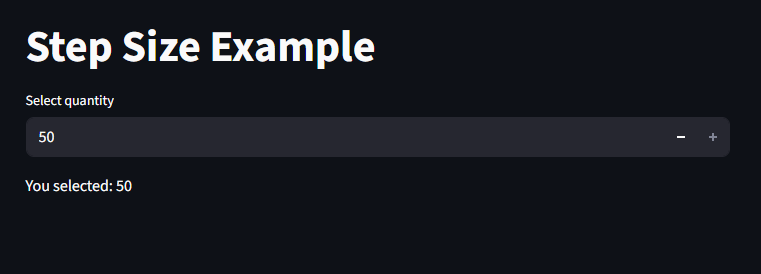
Step Size
The step parameter defines how much the value increases or decreases when clicking the uo and down arrows.
This is great for ticket counters, inventory inputs, budget increments, e.t.c
import streamlit as st
st.title("Step Size Example")
amount = st.number_input("Select quantity", min_value=0, max_value=50, step=5)
st.write(f"You selected: {amount}")
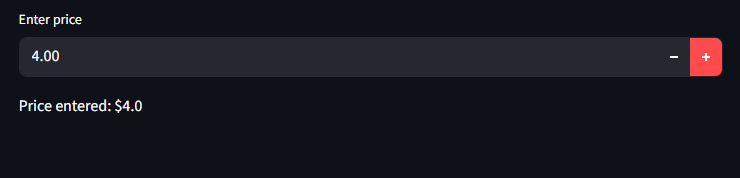
Working with Floats and Integers
Streamlit infers the data type by default, but you can force integers or floats
Here we use a float input
import streamlit as st
price = st.number_input("Enter price", min_value=0.0, max_value=1000.0, step=0.5)
st.write(f"Price entered: ${price}")
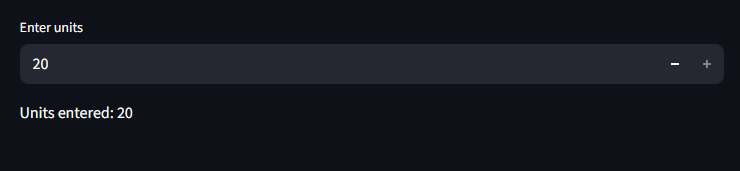
Here we use an integer input
import streamlit as st
units = st.number_input("Enter units", min_value=1, max_value=20, step=1)
st.write(f"Units entered: {units}")
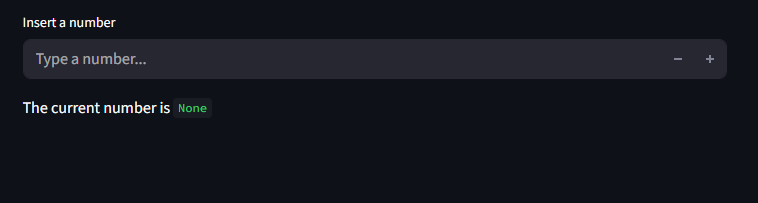
Using None
Instead of initializing an empty number input, use None as the value
It is good to validate business logic even if you set the min and max
import streamlit as st
number = st.number_input(
"Insert a number", value=None, placeholder="Type a number..."
)
st.write("The current number is ", number)
Handling Validation.
We can validate users input manually
import streamlit as st
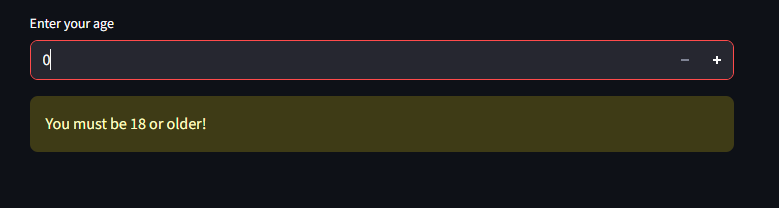
age = st.number_input("Enter your age", min_value=0, max_value=120)
if age < 18:
st.warning("You must be 18 or older!")
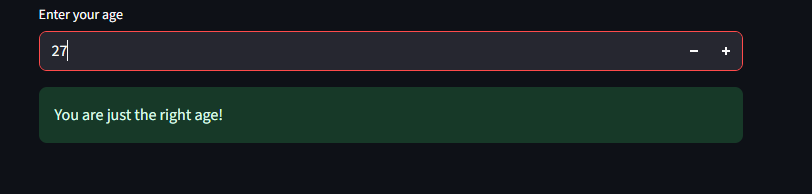
else:
st.success("You are just the right age!")
Using Number Inputs Inside Forms
Forms allow’s ypu to group multiple inputs and submit them together
import streamlit as st
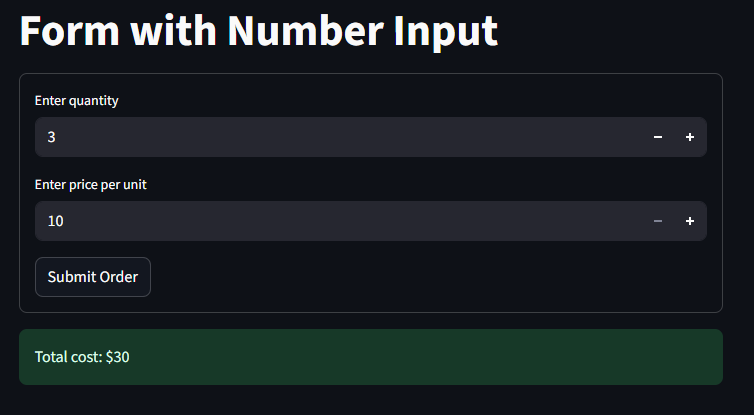
st.title("Form with Number Input")
with st.form("order_form"):
quantity = st.number_input("Enter quantity", min_value=1, max_value=10)
price = st.number_input("Enter price per unit", min_value=10, max_value=100)
submitted = st.form_submit_button("Submit Order")
if submitted:
total = quantity * price
st.success(f"Total cost: ${total}")
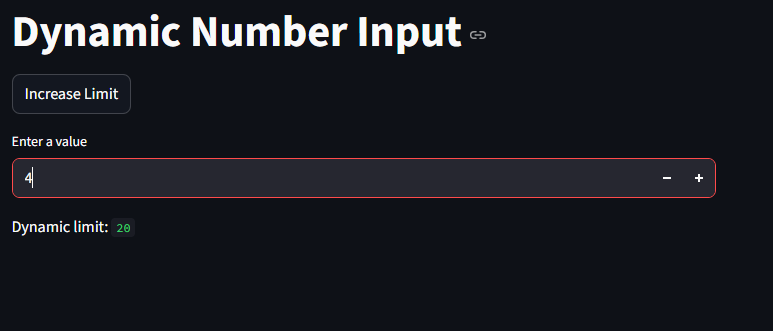
Dynamic Number Inputs with Session State
You can make number inputs dynamic based on user actions.
import streamlit as st
st.title("Dynamic Number Input")
if "counter" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.counter = 0
if st.button("Increase Limit"):
st.session_state.counter += 10
value = st.number_input("Enter a value", min_value=0, max_value=st.session_state.counter)
st.write("Dynamic limit:", st.session_state.counter)