Python Augmented Matrix
import numpy as np
Example 1
# Define coefficient matrix A and constant vector b
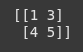
A = np.array([[1, 3], [4, 5]])
print(A)
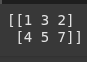
B = np.array([[2], [7]])
# Augmented matrix
augmented_matrix = np.column_stack((A, B))
print(augmented_matrix)
Example 2
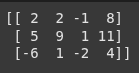
A = np.array([[2, 2, -1], [5, 9, 1], [-6, 1, -2]])
B = np.array([[8], [11], [4]])
augmented_matrix = np.column_stack((A, B))
print(augmented_matrix)
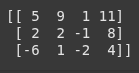
row operations
# Swapping two rows
augmented_matrix[[0, 1]] = augmented_matrix[[1, 0]]
print(augmented_matrix)
Multiply the first row by 3
augmented_matrix[0] = augmented_matrix[0] * 3
print(augmented_matrix)

add: 2nd row to the first
augmented_matrix[0] = augmented_matrix[0] + augmented_matrix[1]
print(augmented_matrix)

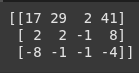
subtract 2nd row from the 3rd
augmented_matrix[2] = augmented_matrix[2] - augmented_matrix[1]
print(augmented_matrix)
df.loc[idx]
Ryan is a Data Scientist at a fintech company, where he focuses on fraud prevention in underwriting and risk. Before that, he worked as a Data Analyst at a tax software company. He holds a degree in Electrical Engineering from UCF.
