n8n rss feed node
If you want to pull stories, trigger automations from publications, or turn feeds into newsletters, Slack posts, WordPress drafts or AI summaries — n8n’s RSS nodes are a compact, powerful way to do it. This article explains what the RSS nodes do, how they differ, detailed setup options, scheduling modes, common workflows, troubleshooting, and best practices.
Before we start, if you are looking for help with a n8n project, we are taking on customers. Head over to our n8n Automation Engineer page.
Quick overview : Which nodes exist and what they do
RSS Read (aka RSS Feed Read)
A non-trigger node that fetches items from a given RSS/Atom URL on demand. Use it when you want to pull a feed as part of a workflow run (for example, called from a Schedule Trigger or Webhook). It returns parsed items (title, link, content, published date, etc.).
RSS Feed Trigger
A trigger node that polls an RSS/Atom URL and starts a workflow whenever new items are found. It detects items published after the node’s last run and emits only those; perfect for continuous automations like “send me an email for each new post.”
When to use Read vs Trigger
Use RSS Read when you want to fetch a feed as part of a scheduled or on-demand workflow (e.g., nightly aggregation).
Use RSS Feed Trigger when you want workflows to start automatically as new items appear (near-real-time automations).
Node parameters & options
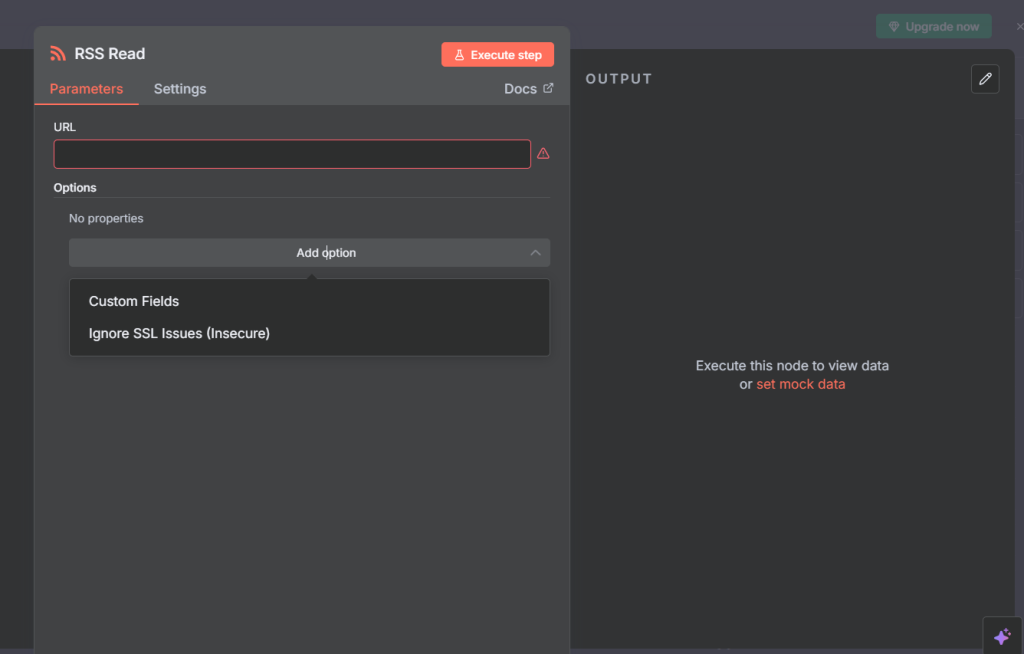
RSS Read node (key fields)
URL — RSS or Atom feed URL (mandatory).
Ignore SSL Issues — useful for internal/self-signed feeds.
Output — Returns an array of items (title, link, content, published date, etc.).
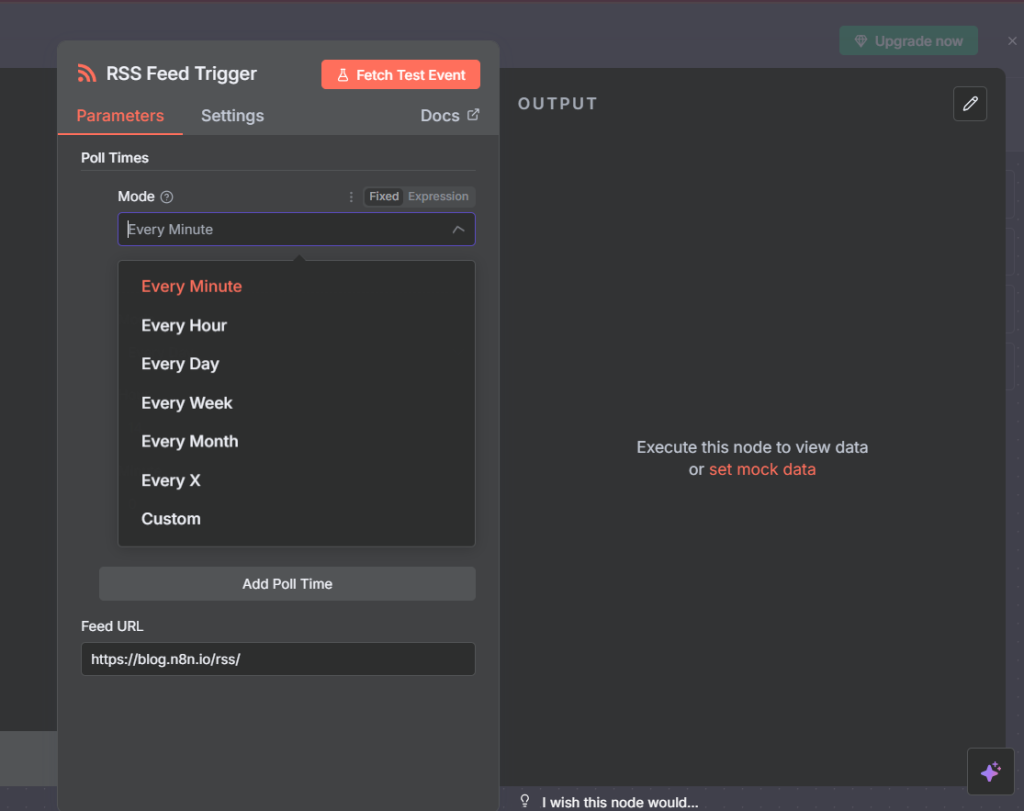
RSS Feed Trigger node (key configuration)
The RSS Feed Trigger node starts workflows automatically whenever new feed items appear. Its power lies in flexible scheduling.
Core Parameters
Feed URL — the RSS/Atom feed to poll.
Poll Times (Mode) — defines how often to check the feed.
Polling Modes
Every Hour
Minute (0–59): choose the exact minute of each hour.
Every Day
Hour (0–23) and Minute (0–59): choose exact daily time.
Every Week
Weekday (0–6; Sunday–Saturday), Hour, Minute.
Every Month
Day of Month (1–31), Hour, Minute.
Every X
Value + Unit (Minutes or Hours). Example: every 15 minutes, or every 2 hours.
Custom (Cron Expression)
Full cron flexibility, including seconds.
Format:
second minute hour day-of-month month day-of-week

Typical workflows / real-world examples
Turn RSS → Email newsletter
Trigger: RSS Feed Trigger
Collect new items → Format → Send via Gmail/SMTP.
n8n template: “Turn any RSS feed into email.”
Aggregate multiple feeds nightly
Schedule Trigger → Loop feed URLs → RSS Read → Filter & sort → Summarize with OpenAI → Store/send.
Auto-post RSS items to WordPress / LinkedIn
RSS Feed Trigger → Format → WordPress/LinkedIn node.
Create an RSS feed from scraped content
HTTP Request + HTML Parse → Construct RSS XML → Serve from storage/endpoint.
Deduplication & State
Triggers: automatically compare new vs old items using timestamps or last-run markers. Feeds with unreliable
pubDatemay cause duplicates/missed items.Read nodes: fetch all items every time. For recurring checks, you must dedupe manually (e.g., store GUIDs/links in a database).
Example 1
Rss feed trigger.
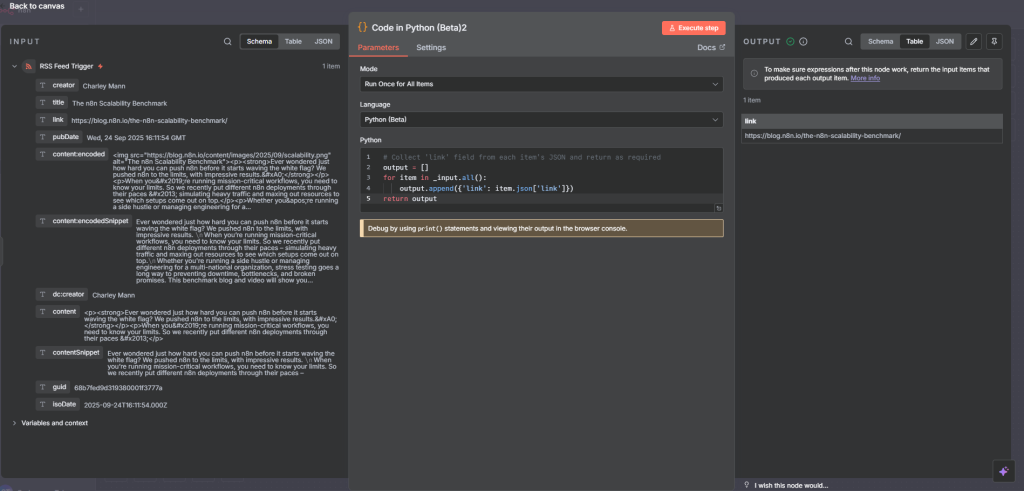
Let’s create a simple trigger that runs every time a new article is added. It runs every minute
we start by adding the rss feed trigger node
Lets add one more step just to display only the links.
full flow
Example 2
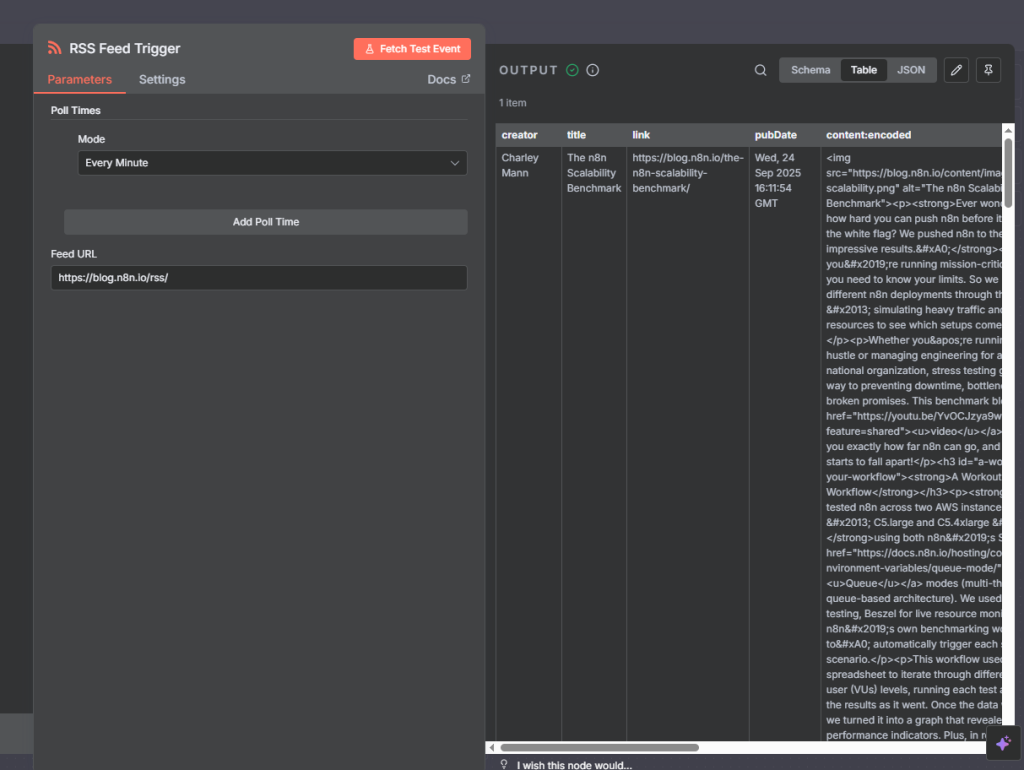
Fetch RSS Feed
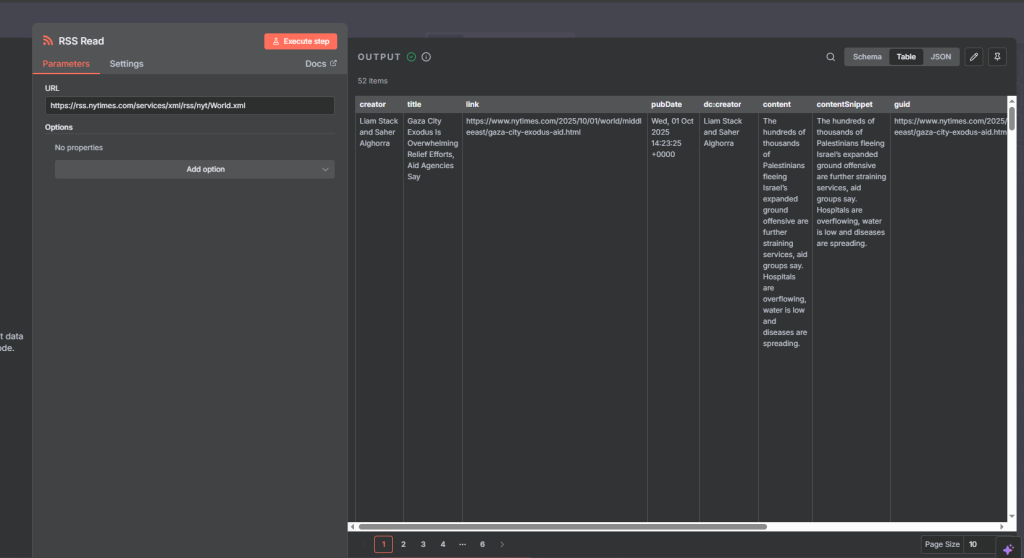
RSS Feed Read Node
Add RSS Feed Read node.
In Feed URL, paste an RSS feed (example:
https://rss.nytimes.com/services/xml/rss/nyt/World.xml).This pulls the latest articles as items.
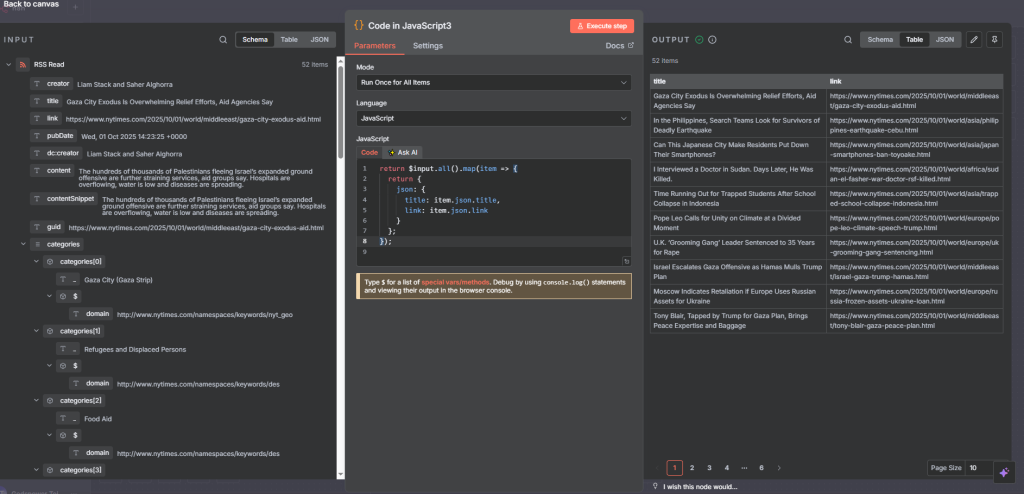
(Optional) CodeNode – Format Output
If you want only the title + link, add a Function node:
fullflow
Best practices checklist
Prefer RSS Feed Trigger for real-time automations; use RSS Read for scheduled/one-off runs.
Always test feeds for consistent
pubDate/GUIDs.Use SplitInBatches for multiple feeds.
Store deduplication metadata externally for resilience.
Respect polling intervals — don’t overwhelm feed servers.
Final thought
The RSS Feed Trigger and RSS Read nodes in n8n are deceptively simple yet powerful. Together, they can power anything from personal newsletters to large-scale AI-enhanced content pipelines. The main challenges you’ll face are deduplication and feed quality — but with proper configuration and scheduling, RSS automation becomes both reliable and scalable.
Thank you for reading this article. Make sure to check out our other n8n content on the website. If you need any help with n8n workflows we are taking on customers so reach out
