Streamlit Logging
Logging is a way to keep track of what happens inside your Streamlit app.
It helps you:
Fix bugs while you’re developing.
Keep an eye on user events and interactions.
Keep track of the phases in data processing.
In Production, keep track of warnings and serious problems.
Streamlit uses Python’s built-in logging module under the hood.
Need a Streamlit developer? Click Here
Streamlit Logging Method
| Log Level | Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| DEBUG | logger.debug(msg) | Detailed information, useful for debugging |
| INFO | logger.info(msg) | General app flow messages |
| WARNING | logger.warning(msg) | Something unexpected happened but the app still works |
| ERROR | logger.error(msg) | A function or process failed |
| CRITICAL | logger.critical(msg) | A serious failure; app stability may be compromised |
Basic Setup
Messages show up in the console where you execute streamlit run app.py.
The default log level for Streamlit is INFO.
import streamlit as st
import logging
# Configure logging
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.DEBUG,
format="%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s"
)
# Create a logger instance
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
st.title("Streamlit Logging Example")
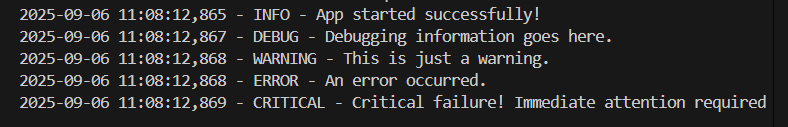
logger.info("App started successfully!")
logger.debug("Debugging information goes here.")
logger.warning("This is just a warning.")
logger.error("An error occurred.")
logger.critical("Critical failure! Immediate attention required.")
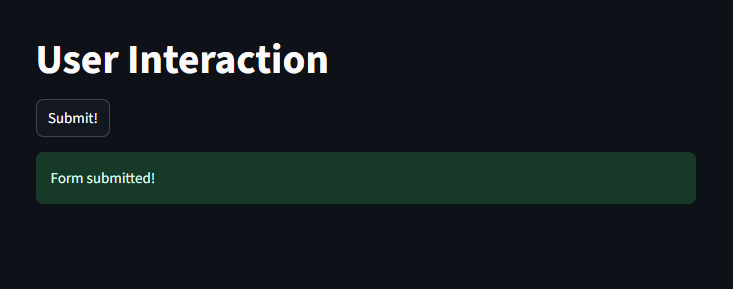
Example with User Interaction Logging with Button
import streamlit as st
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
st.title("User Interaction Logging with Button")
if st.button("Submit!"):
logger.info("User clicked the Submit button")
st.success("Form submitted!")

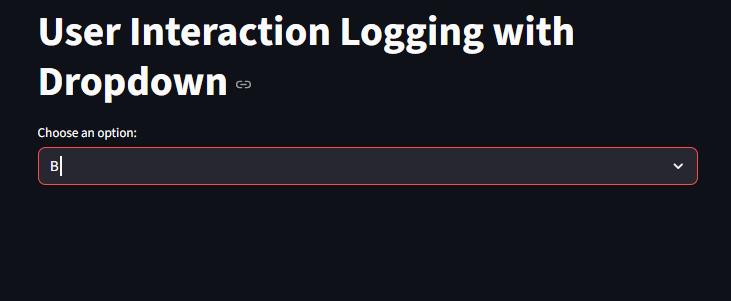
Example with User Interaction Logging with Dropdown
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
st.title("User Interaction Logging with Dropdown")
option = st.selectbox("Choose an option:", ["A", "B", "C"])
logger.info(f"User selected: {option}")
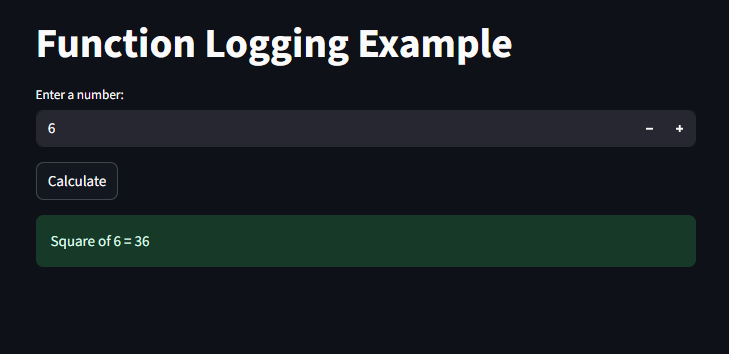
Example with Logging Inside Functions
import streamlit as st
import logging
import time
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
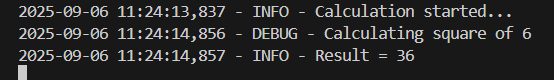
def calculate_square(n):
logger.debug(f"Calculating square of {n}")
result = n ** 2
logger.info(f"Result = {result}")
return result
st.title("Function Logging Example")
number = st.number_input("Enter a number:", 1, 100, 5)
if st.button("Calculate"):
logger.info("Calculation started...")
time.sleep(1)
result = calculate_square(number)
st.success(f"Square of {number} = {result}")
Logging to a File
By default, Streamlit logs appear only in the terminal, But we can store them in a file also.
import streamlit as st
import logging
import os
# Get absolute path for app.log
log_file = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "app.log")
# Remove default Streamlit handlers to prevent duplication issues
for handler in logging.root.handlers[:]:
logging.root.removeHandler(handler)
# Configure logging properly
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.DEBUG,
format="%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s",
handlers=[
logging.FileHandler(log_file), # Save logs to app.log
logging.StreamHandler() # Show logs in terminal
]
)
# Get logger
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# Streamlit UI
st.title("Logging with Streamlit")
logger.info("App started successfully!")
logger.warning("This is just a warning.")
logger.error("An error occurred.")
logger.critical("Critical failure! Immediate attention required.")
st.success(f"Logs saved to: **{log_file}**")
