Streamlit Tabs
Tabs in Streamlit allow’s us to organize content into separate views inside the same app
They are useful for dashboards, multi-steps forms, reports, and when you want to avoid clutter.
Need a Streamlit developer: Click here
Some Basic usage of streamlit tab
we use st.tabs to create tabs in streamlit
we can use the with notation to insert any element into a tab
import streamlit as st
st.title("Streamlit Tabs Example")
tab1, tab2, tab3 = st.tabs(["Home", "About", "Charts"])
with tab1:
st.header("Home")
st.write("This is Home")
with tab2:
st.header("About")
st.write("This is About")
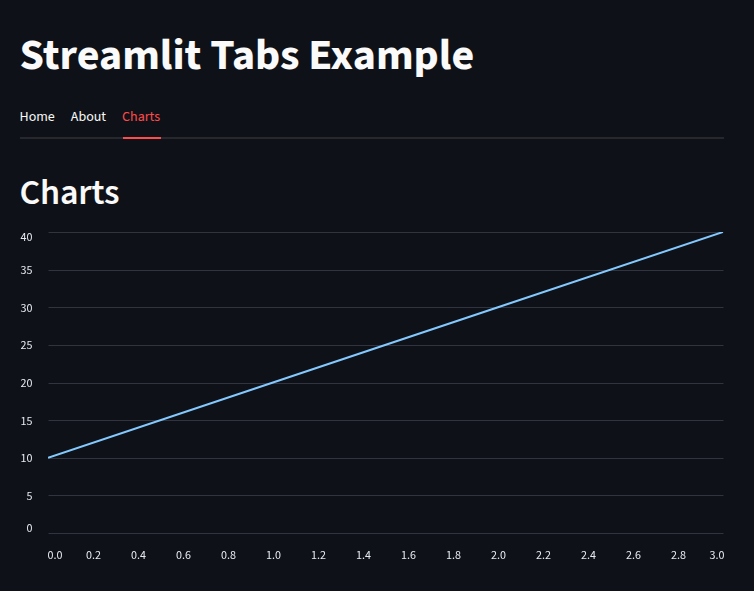
with tab3:
st.header("Charts")
st.line_chart({"Sales": [10, 20, 30, 40]})


We can also add media and Images
import streamlit as st
tab1, tab2, tab3 = st.tabs(["Cat", "Dog", "Owl"])
with tab1:
st.header("A cat")
st.image("https://static.streamlit.io/examples/cat.jpg", width=200)
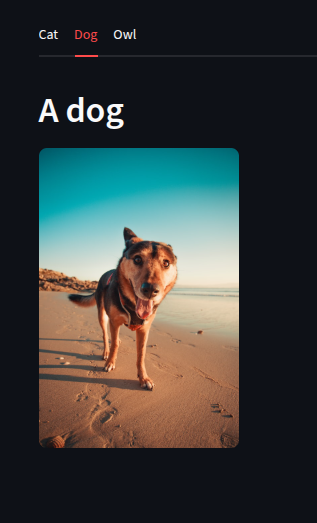
with tab2:
st.header("A dog")
st.image("https://static.streamlit.io/examples/dog.jpg", width=200)
with tab3:
st.header("An owl")
st.image("https://static.streamlit.io/examples/owl.jpg", width=200)


Tabs inside Tabs (Nested Tabs)
Here, we are creating tabs inside tabs
import streamlit as st
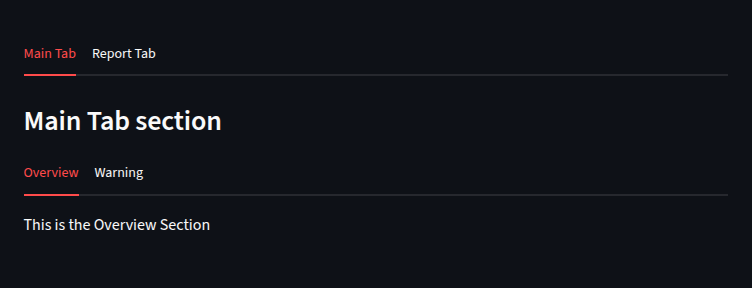
tab1, tab2 = st.tabs(["Main Tab", "Report Tab"])
with tab1:
st.subheader("Main Tab section")
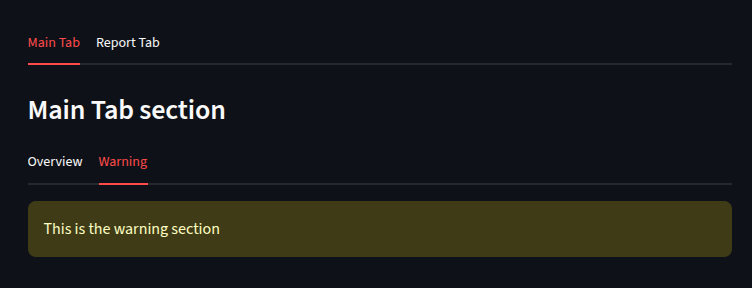
subtab1, subtab2 = st.tabs(["Overview", "Warning"])
with subtab1:
st.write("This is the Overview Section")
with subtab2:
st.warning("This is the warning section")
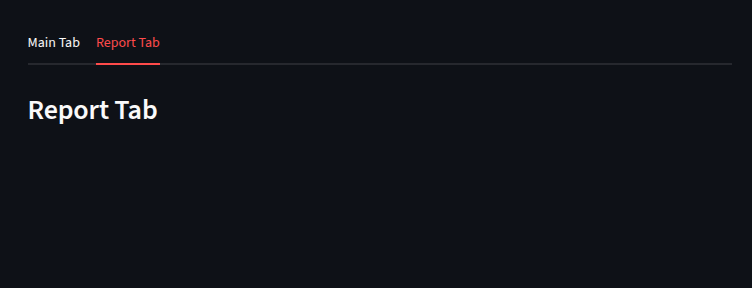
with tab2:
st.subheader("Report Tab")
st.dialog("No report available")
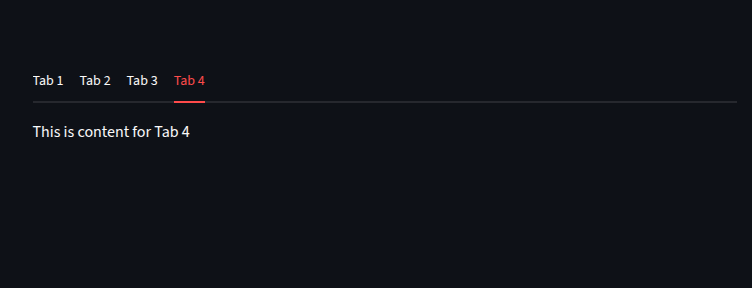
Dynamic Tabs with Loops
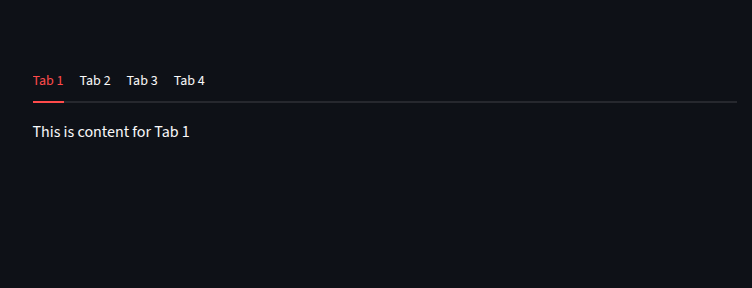
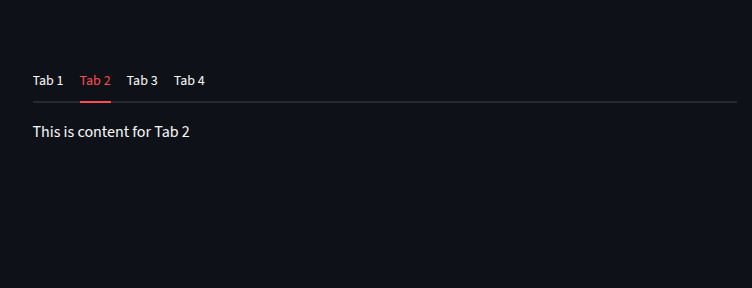
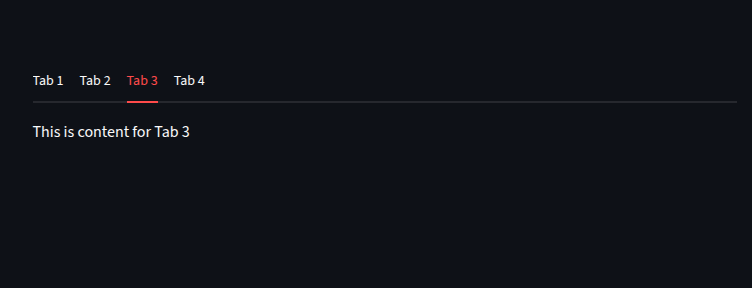
We can create dynamic tabs
import streamlit as st
tabs = st.tabs([f"Tab {i}" for i in range(1, 5)])
for i, tab in enumerate(tabs):
with tab:
#for each tab we display the text.
st.write(f"This is content for Tab {i+1}")
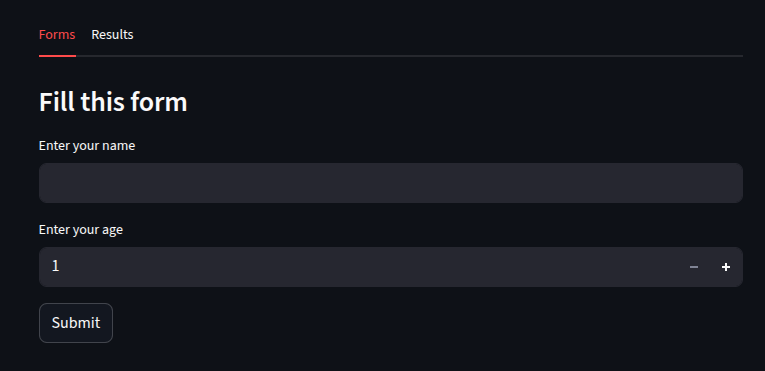
Tabs with Widgets
let’s create an interactive tab
import streamlit as st
tab1, tab2 = st.tabs(["Forms", "Results"])
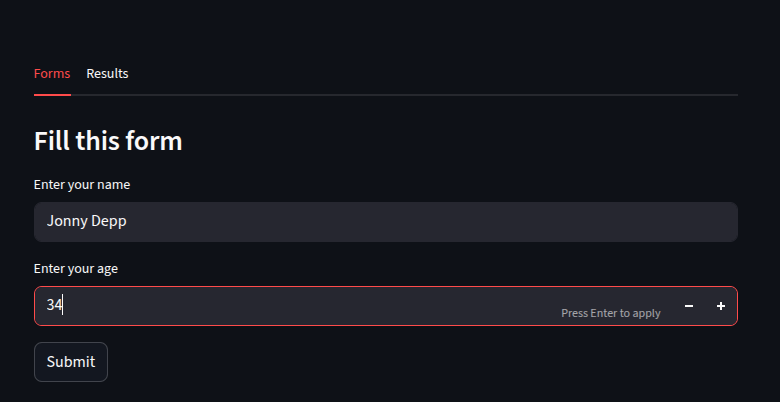
with tab1:
st.subheader("Fill this form")
name = st.text_input("Enter your name")
age = st.number_input("Enter your age", min_value=1, max_value=150)
submit = st.button("Submit")
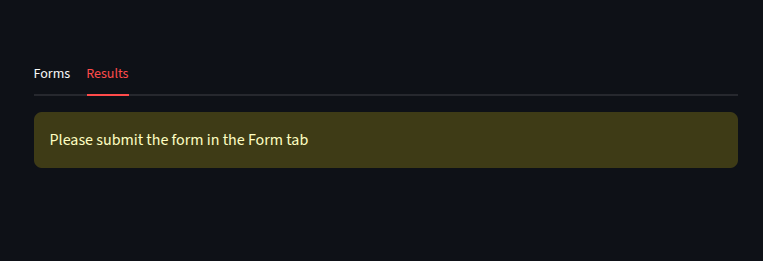
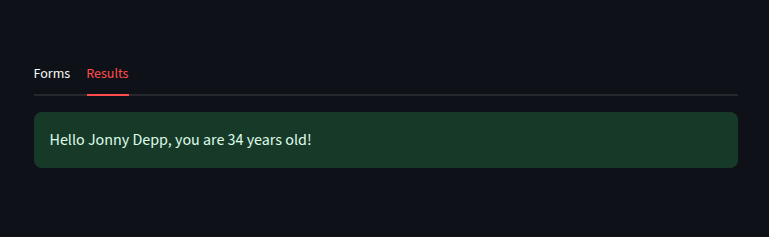
with tab2:
if submit:
st.success(f"Hello {name}, you are {age} years old!")
else:
st.warning("Please submit the form in the Form tab")
Tabs for Multi-Page Dashboard
import streamlit as st
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Dummy data
df = pd.DataFrame(
np.random.randn(10, 3),
columns=["A", "B", "C"]
)
tab1, tab2, tab3 = st.tabs(["📊 Data", "📈 Charts", "⚙️ Settings"])
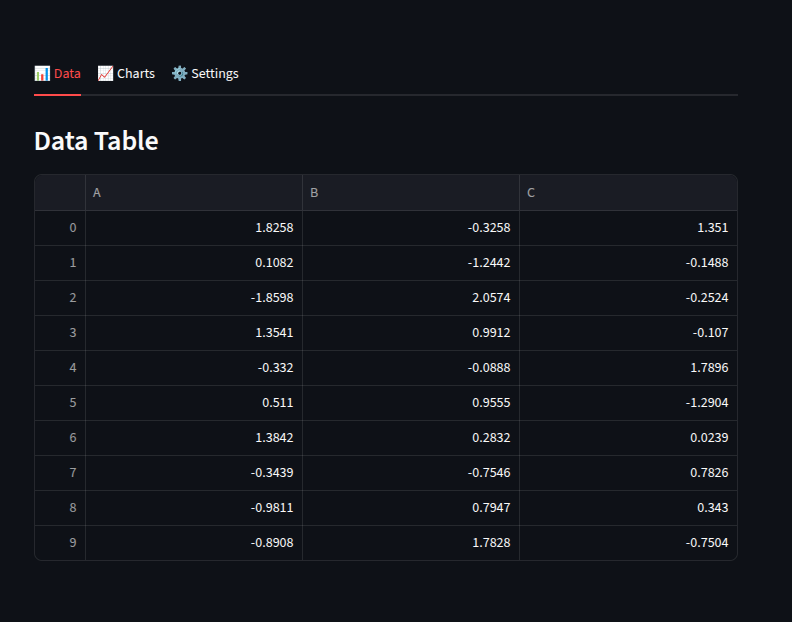
with tab1:
st.write("### Data Table")
st.dataframe(df)
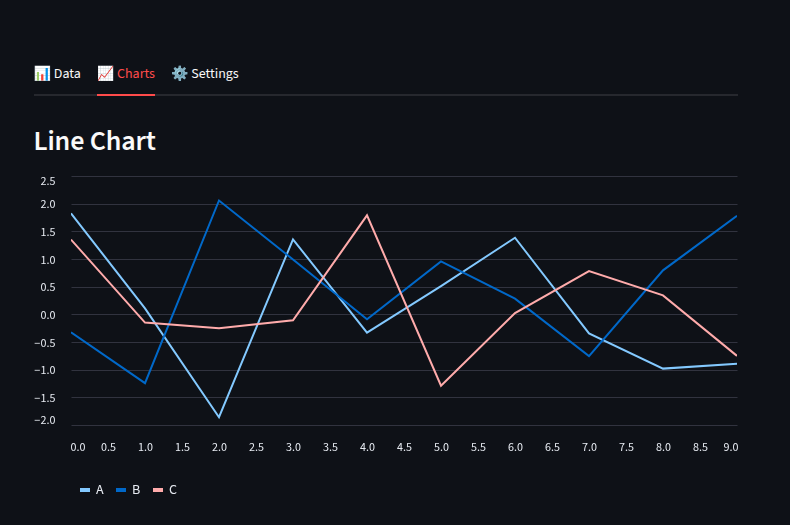
with tab2:
st.write("### Line Chart")
st.line_chart(df)
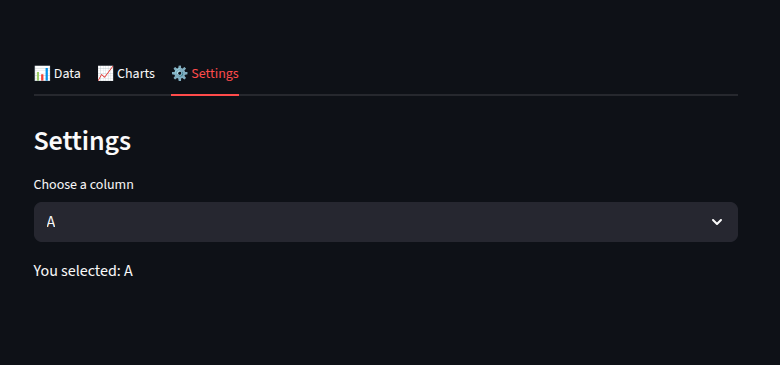
with tab3:
st.write("### Settings")
option = st.selectbox("Choose a column", df.columns)
st.write(f"You selected: {option}")
Conclusion
Keep related content together (don’t overload one tab).
For larger apps → use Streamlit multipage apps (tabs are best for smaller sections).
Want to learn more about Streamlit?: Click here
Watch videos on Streamlit:
